Primary angioplasty in acute myocardial infarction with right bundle branch block: should new onset right bundle branch block be added to future guidelines as an indication for reperfusion therapy?
- PMID: 21890488
- PMCID: PMC3249219
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr291
Primary angioplasty in acute myocardial infarction with right bundle branch block: should new onset right bundle branch block be added to future guidelines as an indication for reperfusion therapy?
Abstract
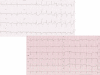
Aims: The current guidelines recommend reperfusion therapy in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) with ST-segment elevation or left bundle branch block (LBBB). Surprisingly, the right bundle branch block (RBBB) is not listed as an indication for reperfusion therapy. This study analysed patients with AMI presenting with RBBB [with or without left anterior hemiblock (LAH) or left posterior hemiblock (LPH)] and compared them with those presenting with LBBB or with other electrocardiographic (ECG) patterns. The aim was to describe angiographic patterns and primary angioplasty use in AMI patients with RBBB.
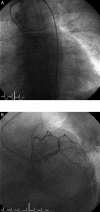
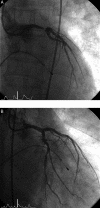
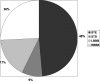
Methods and results: A cohort of 6742 patients with AMI admitted to eight participating hospitals was analysed. Baseline clinical characteristics, ECG patterns, coronary angiographic, and echocardiographic data were correlated with the reperfusion therapies used and with in-hospital outcomes. Right bundle branch block was present in 6.3% of AMI patients: 2.8% had RBBB alone, 3.2% had RBBB + LAH, and 0.3% had RBBB + LPH. TIMI flow 0 in the infarct-related artery was present in 51.7% of RBBB patients vs. 39.4% of LBBB patients (P = 0.023). Primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was performed in 80.1% of RBBB patients vs. 68.3% of LBBB patients (P< 0.001). In-hospital mortality of RBBB patients was similar to LBBB (14.3 vs. 13.1%, P = 0.661). Patients with new or presumably new blocks had the highest (LBBB 15.8% and RBBB 15.4%) incidence of cardiogenic shock from all ECG subgroups. Percutaneous coronary intervention was done more frequently (84.8%) in patients with new or presumably new RBBB when compared with other patients with blocks (old RBBB 66.0%, old LBBB 62.3%, new or presumably new LBBB 73.0%). In-hospital mortality was highest (18.8%) among patients presenting with new or presumably new RBBB, followed by new or presumably new LBBB (13.2%), old LBBB (10.1%), and old RBBB (6.4%). Among 35 patients with acute left main coronary artery occlusion, 26% presented with RBBB (mostly with LAH) on the admission ECG.
Conclusion: Acute myocardial infarction with RBBB is frequently caused by the complete occlusion of the infarct-related artery and is more frequently treated with primary PCI when compared with AMI + LBBB. In-hospital mortality of patients with AMI and RBBB is highest from all ECG presentations of AMI. Restoration of coronary flow by primary PCI may lead to resolution of the conduction delay on the discharge ECG. Right bundle branch block should strongly be considered for listing in future guidelines as a standard indication for reperfusion therapy, in the same way as LBBB.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic differences between different types of bundle branch block during the early phase of acute myocardial infarction: insights from the Hirulog and Early Reperfusion or Occlusion (HERO)-2 trial.Eur Heart J. 2006 Jan;27(1):21-8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehi622. Epub 2005 Nov 3. Eur Heart J. 2006. PMID: 16269419 Clinical Trial.
-
Right, but not left, bundle branch block is associated with large anteroseptal scar.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Sep 10;62(11):959-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.04.060. Epub 2013 May 22. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23707313 Free PMC article.
-
Left anterior hemiblock in acute myocardial infarction. Incidence and clinical significance in relation to the presence of bundle branch block and to the absence of intraventricular conduction defects.Acta Med Scand. 1978;203(6):529-34. Acta Med Scand. 1978. PMID: 665320
-
Bundle branch blocks and/or hemiblocks complicating acute myocardial ischemia or infarction.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2018 Aug;52(3):287-292. doi: 10.1007/s10840-018-0430-3. Epub 2018 Aug 22. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2018. PMID: 30136134 Review.
-
[The importance of left bundle branch block in the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction].Medicina (Kaunas). 2003;39(1):15-20. Medicina (Kaunas). 2003. PMID: 12576761 Review. Lithuanian.
Cited by
-
The 'qRBBB myocardial infarction': Unwrapping an old enigma.Indian Heart J. 2024 Jan-Feb;76(1):57-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2024.01.005. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Indian Heart J. 2024. PMID: 38199561 Free PMC article.
-
New permanent bundle-branch block and long-term prognosis of patients with new onset ST-elevation myocardial infarction who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention.Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 22;13:892623. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.892623. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36072847 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-hospital treatment of patients with acute coronary syndrome: Recommendations for medical emergency teams. Expert position update 2022.Cardiol J. 2022;29(4):540-552. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2022.0026. Epub 2022 May 6. Cardiol J. 2022. PMID: 35514089 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Combining electrocardiographic criteria for predicting acute total left main coronary artery occlusion.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 11;9:936687. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.936687. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36035902 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond STEMI-NSTEMI Paradigm: Dante Pazzanese's Proposal for Occlusion Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024 Jul 15;121(5):e20230733. doi: 10.36660/abc.20230733. eCollection 2024. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39016396 Free PMC article. Review. English, Portuguese.
References
-
- Wong CK, Stewart RAH, Gao W, French JK, Raffel C, White HD for the Hirulog and Early Reperfusion or Occlusion (HERO-2) Trial Investigators. Prognostic differences between different types of bundle branch block during the early phase of acute myocardial infarction: insights from the Hirulog and Early Reperfusion or Occlusion (HERO)-2 trial. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Van de Werf F, Bax J, Betriu A, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Crea F, Falk V, Filippatos G, Fox K, Huber K, Kastrati A, Rosengren A, Steg PG, Tubaro M, Verheugt F, Weidinger F, Weis M, Vahanian A, Camm J, De Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Tendera M, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL, Aguirre FV, Al-Attar N, Alegria E, Andreotti F, Benzer W, Breithardt O, Danchin N, Di Mario C, Dudek D, Gulba D, Halvorsen S, Kaufmann P, Kornowski R, Lip GY, Rutten F. Management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with persistent ST-segment elevation: the Task Force on the Management of ST-Segment Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2008;29:2909–2945. - PubMed
-
- Antman EM, Anbe DT, Armstrong PW, Bates ER, Green LA, Hand M, Hochman JS, Krumholz HM, Kushner FG, Lamas GA, Mullany CJ, Ornato JP, Pearle DL, Sloan MA, Smith SC, Jr, Alpert JS, Anderson JL, Faxon DP, Fuster V, Gibbons RJ, Gregoratos G, Halperin JL, Hiratzka LF, Hunt SA, Jacobs AK. ACC/AHA Guidelines for the Management of Patients With ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:671–719. - PubMed
-
- Gould L, Venkataraman K, Mohhamad N, Gomprecht RF. Prognosis of right bundle-branch block in acute myocardial infarction. JAMA. 1972;219:502–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

