Rheumatoid arthritis and pregnancy: evolution of disease activity and pathophysiological considerations for drug use
- PMID: 21890617
- PMCID: PMC3198908
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker302
Rheumatoid arthritis and pregnancy: evolution of disease activity and pathophysiological considerations for drug use
Abstract
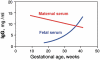
It has long been known that pregnancy and childbirth have a profound effect on the disease activity of rheumatic diseases. For clinicians, the management of patients with RA wishing to become pregnant involves the challenge of keeping disease activity under control and adequately adapting drug therapy during pregnancy and post-partum. This article aims to summarize the current evidence on the evolution of RA disease activity during and after pregnancy and the use of anti-rheumatic drugs around this period. Of recent interest is the potential use of anti-TNF compounds in the preconception period and during pregnancy. Accumulating experience with anti-TNF therapy in other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, such as Crohn's disease, provides useful insights for the use of TNF blockade in pregnant women with RA, or RA patients wishing to become pregnant.
Figures

References
-
- Hench PS. The ameliorating effect of pregnancy on chronic atrophic (infectious rheumatoid) arthritis, fibrositis and intermittent hydrarthritis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1938;13:161–7.
-
- Golding A, Haque UJ, Giles JT. Rheumatoid arthritis and reproduction. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2007;33:319–43. - PubMed
-
- Klipple GL, Cecere FA. Rheumatoid arthritis and pregnancy. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1989;15:213–39. - PubMed

