Barcoded primers used in multiplex amplicon pyrosequencing bias amplification
- PMID: 21890669
- PMCID: PMC3209180
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.05220-11
Barcoded primers used in multiplex amplicon pyrosequencing bias amplification
Erratum in
- Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Jan;78(2):612
Abstract
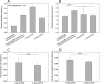
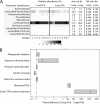
"Barcode-tagged" PCR primers used for multiplex amplicon sequencing generate a thus-far-overlooked amplification bias that produces variable terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) and pyrosequencing data from the same environmental DNA template. We propose a simple two-step PCR approach that increases reproducibility and consistently recovers higher genetic diversity in pyrosequencing libraries.
Figures
References
-
- Amend A. S., Seifert K. A., Bruns T. D. 2010. Quantifying microbial communities with 454 pyrosequencing: does read abundance count? Mol. Ecol. 19:5555–5565 - PubMed
-
- Engelbrektson A., et al. 2010. Experimental factors affecting PCR-based estimates of microbial species richness and evenness. ISME J. 4:642–647 - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Alvarez V., Teal T. K., Schmidt T. M. 2009. Systematic artifacts in metagenomes from complex microbial communities. ISME J. 3:1314–1317 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

