The Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 increases erythrocyte deformability and low oxygen tension-induced ATP release
- PMID: 21890695
- PMCID: PMC3213963
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00603.2011
The Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 increases erythrocyte deformability and low oxygen tension-induced ATP release
Abstract
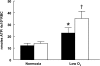
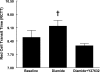
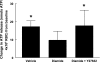
Low oxygen (O(2)) tension and mechanical deformation are stimuli for ATP release from erythrocytes. It has been shown previously that rabbit erythrocytes made less deformable with diamide, a thiol cross-linking agent, release less ATP in response to low O(2) tension, suggesting a link between these two stimuli. In nonerythroid cells, activation of the Rho/Rho kinase signaling pathway has been reported to decrease cell deformability by altering Rho kinase-dependent cytoskeleton-protein interactions. We investigated the hypothesis that the Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 would increase erythrocyte deformability and thereby increase low O(2) tension-induced ATP release from erythrocytes. Here we show that Y-27632 (1 μM) increases erythrocyte deformability (5%) and increases low O(2) tension-induced ATP release (203%) from healthy human erythrocytes. In addition, we found that, when erythrocytes were made less deformable by incubation with diamide (100 μM), Y-27632 restored both deformability and low O(2) tension-induced ATP release to levels similar to those measured in the absence of diamide. These findings suggest that the Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 is able to reverse the diamide-induced decrease in erythrocyte deformability and rescue low O(2) tension-induced ATP release. These results further support a link between erythrocyte deformability and ATP release in response to low O(2) tension.
Figures


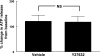
References
-
- An SS, Pennella CM, Gonnabathula A, Chen J, Wang N, Gaestel M, Hassoun PM, Fredberg JJ, Kayyali US. Hypoxia alters biophysical properties of endothelial cells via p38 MAPK- and Rho kinase-dependent pathways. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 289: C521–C530, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bergfeld GR, Forrester T. Release of ATP from human erythrocytes in response to a brief period of hypoxia and hypercapnia. Cardiovasc Res 26: 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

