Signal-induced Brd4 release from chromatin is essential for its role transition from chromatin targeting to transcriptional regulation
- PMID: 21890894
- PMCID: PMC3239188
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr698
Signal-induced Brd4 release from chromatin is essential for its role transition from chromatin targeting to transcriptional regulation
Abstract
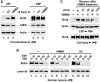
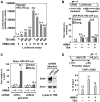
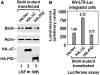
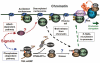
Bromodomain-containing protein Brd4 is shown to persistently associate with chromosomes during mitosis for transmitting epigenetic memory across cell divisions. During interphase, Brd4 also plays a key role in regulating the transcription of signal-inducible genes by recruiting positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) to promoters. How the chromatin-bound Brd4 transits into a transcriptional regulation mode in response to stimulation, however, is largely unknown. Here, by analyzing the dynamics of Brd4 during ultraviolet or hexamethylene bisacetamide treatment, we show that the signal-induced release of chromatin-bound Brd4 is essential for its functional transition. In untreated cells, almost all Brd4 is observed in association with interphase chromatin. Upon treatment, Brd4 is released from chromatin, mostly due to signal-triggered deacetylation of nucleosomal histone H4 at acetylated-lysine 5/8 (H4K5ac/K8ac). Through selective association with the transcriptional active form of P-TEFb that has been liberated from the inactive multi-subunit complex in response to treatment, the released Brd4 mediates the recruitment of this active P-TEFb to promoter, which enhances transcription at the stage of elongation. Thus, through signal-induced release from chromatin and selective association with the active form of P-TEFb, the chromatin-bound Brd4 switches its role to mediate the recruitment of P-TEFb for regulating the transcriptional elongation of signal-inducible genes.
© The Author(s) 2011. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures



References
-
- Selth LA, Sigurdsson S, Svejstrup JQ. Transcript Elongation by RNA polymerase II. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010;79:271–293. - PubMed
-
- Peterlin BM. Transcription elongation takes central stage: the P-TEFb connection. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:2933–2934. - PubMed
-
- Price DH. Poised polymerases: on your mark … get set … go! Mol. Cell. 2008;30:7–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

