Dynamic regulation of glucocorticoid signalling in health and disease
- PMID: 21891790
- PMCID: PMC3281495
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker215
Dynamic regulation of glucocorticoid signalling in health and disease
Abstract
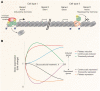
Activation of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) by endogenous and synthetic glucocorticoids regulates hundreds of genes to control regulatory networks in development, metabolism, cognition and inflammation. Elucidation of the mechanisms that regulate glucocorticoid action has highlighted the dynamic nature of hormone signalling and provides novel insights into genomic glucocorticoid actions. The major factors that regulate GR function include chromatin structure, epigenetics, genetic variation and the pattern of glucocorticoid hormone secretion. We review our current understanding of the mechanisms that contribute to GR signalling and how these contribute to glucocorticoid sensitivity, resistance and side effects.
Figures


References
-
- Corrigan CJ, Brown PH, Barnes NC, et al. Glucocorticoid resistance in chronic asthma. Glucocorticoid pharmacokinetics, glucocorticoid receptor characteristics, and inhibition of peripheral blood T cell proliferation by glucocorticoids in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;144:1016–25. - PubMed
-
- Kirkham BW, Corkill MM, Davison SC, Panayi GS. Response to glucocorticoid treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: in vitro cell mediated immune assay predicts in vivo responses. J Rheumatol. 1991;18:821–5. - PubMed
-
- Faubion WA, Jr, Loftus EV, Jr, Harmsen WS, Zinsmeister AR, Sandborn WJ. The natural history of corticosteroid therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:255–60. - PubMed
-
- Greenstein B. Steroid resistance: implications for lupus. Lupus. 1994;3:143. - PubMed
-
- Leung DY, Bloom JW. Update on glucocorticoid action and resistance. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 111:3–22. quiz 23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

