Oncogenic IL7R gain-of-function mutations in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 21892159
- PMCID: PMC7424552
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.924
Oncogenic IL7R gain-of-function mutations in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
Interleukin 7 (IL-7) and its receptor, formed by IL-7Rα (encoded by IL7R) and γc, are essential for normal T-cell development and homeostasis. Here we show that IL7R is an oncogene mutated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). We find that 9% of individuals with T-ALL have somatic gain-of-function IL7R exon 6 mutations. In most cases, these IL7R mutations introduce an unpaired cysteine in the extracellular juxtamembrane-transmembrane region and promote de novo formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds between mutant IL-7Rα subunits, thereby driving constitutive signaling via JAK1 and independently of IL-7, γc or JAK3. IL7R mutations induce a gene expression profile partially resembling that provoked by IL-7 and are enriched in the T-ALL subgroup comprising TLX3 rearranged and HOXA deregulated cases. Notably, IL7R mutations promote cell transformation and tumor formation. Overall, our findings indicate that IL7R mutational activation is involved in human T-cell leukemogenesis, paving the way for therapeutic targeting of IL-7R-mediated signaling in T-ALL.
Figures
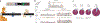

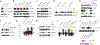
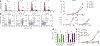
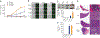
References
-
- Jiang Q et al. Cell biology of IL-7, a key lymphotrophin. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 513–533 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Fry TJ & Mackall CL The many faces of IL-7: from lymphopoiesis to peripheral T cell maintenance. J. Immunol. 174, 6571–6576 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Puel A, Ziegler SF, Buckley RH & Leonard WJ Defective IL7R expression in T(−)B(+)NK(+) severe combined immunodeficiency. Nat. Genet. 20, 394–397 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

