Invariant natural killer T cells recognize glycolipids from pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria
- PMID: 21892173
- PMCID: PMC3178673
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2096
Invariant natural killer T cells recognize glycolipids from pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria
Abstract
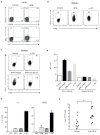
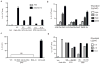
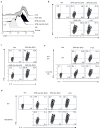
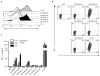
Natural killer T cells (NKT cells) recognize glycolipid antigens presented by CD1d. These cells express an evolutionarily conserved, invariant T cell antigen receptor (TCR), but the forces that drive TCR conservation have remained uncertain. Here we show that NKT cells recognized diacylglycerol-containing glycolipids from Streptococcus pneumoniae, the leading cause of community-acquired pneumonia, and group B Streptococcus, which causes neonatal sepsis and meningitis. Furthermore, CD1d-dependent responses by NKT cells were required for activation and host protection. The glycolipid response was dependent on vaccenic acid, which is present in low concentrations in mammalian cells. Our results show how microbial lipids position the sugar for recognition by the invariant TCR and, most notably, extend the range of microbes recognized by this conserved TCR to several clinically important bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Natural killer T cells: Worth holding on to.Nat Rev Immunol. 2011 Sep 23;11(10):642. doi: 10.1038/nri3075. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21941292 No abstract available.
-
Gram-positive bacteria: a major microbial ‘turn-on’ for invariant NKT cells.Immunotherapy. 2012 Jan;4(1):19. doi: 10.2217/imt.11.152. Immunotherapy. 2012. PMID: 22149997 No abstract available.
References
-
- Taniguchi M, Harada M, Kojo S, Nakayama T, Wakao H. The regulatory role of Valpha14 NKT cells in innate and acquired immune response. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:483–513. - PubMed
-
- Brigl M, Brenner MB. CD1: Antigen Presentation and T Cell Function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:817–890. - PubMed
-
- Godfrey DI, Berzins SP. Control points in NKT-cell development. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:505–518. - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:297–336. - PubMed
-
- Cerundolo V, Silk JD, Masri SH, Salio M. Harnessing invariant NKT cells in vaccination strategies. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:28–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- AI074952/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI45053/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32AI083029/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI070258/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI071922/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AI069296/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI070258/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI070258/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI045053/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI083029/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI074952/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI071922/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI71922/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI074952/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI069276/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

