Human cytomegalovirus microRNA miR-US4-1 inhibits CD8(+) T cell responses by targeting the aminopeptidase ERAP1
- PMID: 21892175
- PMCID: PMC3526977
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2097
Human cytomegalovirus microRNA miR-US4-1 inhibits CD8(+) T cell responses by targeting the aminopeptidase ERAP1
Abstract
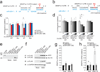
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules present peptides on the cell surface to CD8(+) T cells, which is critical for the killing of virus-infected or transformed cells. Precursors of MHC class I-presented peptides are trimmed to mature epitopes by the aminopeptidase ERAP1. The US2-US11 genomic region of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is dispensable for viral replication and encodes three microRNAs (miRNAs). We show here that HCMV miR-US4-1 specifically downregulated ERAP1 expression during viral infection. Accordingly, the trimming of HCMV-derived peptides was inhibited, which led to less susceptibility of infected cells to HCMV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Our findings identify a previously unknown viral miRNA-based CTL-evasion mechanism that targets a key step in the MHC class I antigen-processing pathway.
Figures


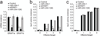

References
-
- Hansen TH, Bouvier M. MHC class I antigen presentation: learning from viral evasion strategies. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:503–513. - PubMed
-
- Haroon N, Inman RD. Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidases: Biology and pathogenic potential. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6:461–467. - PubMed
-
- Saric T, et al. An IFN-gamma-induced aminopeptidase in the ER, ERAP1, trims precursors to MHC class I-presented peptides. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:1169–1176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

