Expression levels of thymidylate synthase, thymidylate phosphorylase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: preliminary study
- PMID: 21892263
- PMCID: PMC3161652
Expression levels of thymidylate synthase, thymidylate phosphorylase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: preliminary study
Abstract
Introduction: Pharyngo-laryngeal tumors classified as T3-4, N0-3, M0, are conventionally treated by mutilating surgery (total (pharyngo)-laryngectomy). Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy with 5-FU/platinum salt can be proposed in an attempt to preserve the larynx. The level of the response to chemotherapy ranges from 36 to 54% of cases. Thus, a large number of patients receive chemotherapy that is ineffective and not free from adverse effects. Three main enzymes are involved in the metabolism of 5-FU: thymidylate synthase (TS), thymidylate phosphorylase (TP) and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD). Several studies suggest that a high level of expression of these three genes correlates with a poor clinical response to 5-FU. The main purpose of our study was to look for a correlation between the levels of expression of the genes for sensitivity to 5-FU (TS, TP, DPD) within the tumor and the clinical response observed after three courses of chemotherapy combining 5-FU/platinum salt in patients presenting with advanced cancer of the pharyngo-larynx.
Methods: This was a prospective genetic study that had required approval from the Ethics Committee. The main assessment criterion was based on the assessment of the clinical response by an ENT panendoscopy and a cervical CT scan, after three courses of chemotherapy. The expression of the genes was determined by quantitative RT-PCR, using total RNA extracted from tumor biopsies taken during the initial panendoscopy.
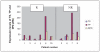
Results: The means calculated, in our study, for the three genes of interest (TS, TP, DPD) were lower in the responder group than those in the non-responder group.
Discussion: Our preliminary findings reveal trends that confirm the hypothesis that the lower the level of expression of the sensitivity genes, the better the clinical response to chemotherapy. They now form part of a larger study that is currently in progress.
Keywords: 5-FU; chemotherapy; genes of sensitivity; pharyngolarynx; squamous cell carcinoma.
Figures


 ) (ARU) depending on clinical response after C3: patient responder (R) or non-responder (NR).
) (ARU) depending on clinical response after C3: patient responder (R) or non-responder (NR).
References
-
- Janot F, Rhein B, Koka VN, Wibault P, Domenge C, Bessede JP, et al. Laryngeal preservation with induction chemotherapy. Experience of two gettec centers, between 1985 and 1995. Ann. Otolaryngol. Chir. Cervicofac. 2002;119:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Lecanu JB, Monceaux G, Perie S, Angelard B, St Guily JL. Conservative surgery in T3-T4 pharyngolaryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: an alternative to radiation therapy and to total laryngectomy for good responders to induction chemotherapy. Laryngoscope. 2000;110:412–6. - PubMed
-
- Johnston PG, Lenz HJ, Leichman CG, Danenberg KD, Allegra CJ, Danenberg PV, et al. Thymidylate synthase gene and protein expression correlate and are associated with 5-fluorouracil, in human colorectal and gastric tumors. Cancer Res. 1995;55:1407–12. - PubMed
-
- Uetake H, Ichikawa W, Takechi T, Fukushima M, Nihei Z, Sugihara K, et al. Relationship between intratumoral dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase activity and gene expression in human colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:2836–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
