Reducible HPMA-co-oligolysine copolymers for nucleic acid delivery
- PMID: 21893178
- PMCID: PMC3240689
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.08.015
Reducible HPMA-co-oligolysine copolymers for nucleic acid delivery
Abstract
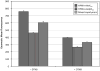
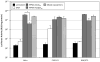
Biodegradability can be incorporated into cationic polymers via use of disulfide linkages that are degraded in the reducing environment of the cell cytosol. In this work, N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide (HPMA) and methacrylamido-functionalized oligo-l-lysine peptide monomers with either a non-reducible 6-aminohexanoic acid (AHX) linker or a reducible 3-[(2-aminoethyl)dithiol] propionic acid (AEDP) linker were copolymerized via reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. Both of the copolymers and a 1:1 (w/w) mixture of copolymers with reducible and non-reducible peptides were complexed with DNA to form polyplexes. The polyplexes were tested for salt stability, transfection efficiency, and cytotoxicity. The HPMA-oligolysine copolymer containing the reducible AEDP linkers was less efficient at transfection than the non-reducible polymer and was prone to flocculation in saline and serum-containing conditions, but was also not cytotoxic at charge ratios tested. Optimal transfection efficiency and toxicity were attained with mixed formulation of copolymers. Flow cytometry uptake studies indicated that blocking extracellular thiols did not restore transfection efficiency and that the decreased transfection of the reducible polyplex is therefore not primarily caused by extracellular polymer reduction by free thiols. The decrease in transfection efficiency of the reducible polymers could be partially mitigated by the addition of low concentrations of EDTA to prevent metal-catalyzed oxidation of reduced polymers.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cathepsin B-sensitive polymers for compartment-specific degradation and nucleic acid release.J Control Release. 2012 Feb 10;157(3):445-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.10.016. Epub 2011 Oct 20. J Control Release. 2012. PMID: 22036879 Free PMC article.
-
HPMA-oligolysine copolymers for gene delivery: optimization of peptide length and polymer molecular weight.J Control Release. 2011 Oct 30;155(2):303-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.07.009. Epub 2011 Jul 14. J Control Release. 2011. PMID: 21782863 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on guanidinated N-3-aminopropyl methacrylamide-N-2-hydroxypropyl methacrylamide co-polymers as gene delivery carrier.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2012;23(1-4):133-52. doi: 10.1163/092050610X545058. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2012. PMID: 22133350
-
HPMA Copolymers: A Versatile Platform for Targeted Peptide Drug Delivery.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 17;15(4):596. doi: 10.3390/biom15040596. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond oncology--application of HPMA copolymers in non-cancerous diseases.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Feb 17;62(2):258-71. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.10.006. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010. PMID: 19909776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The transduction of Coxsackie and Adenovirus Receptor-negative cells and protection against neutralizing antibodies by HPMA-co-oligolysine copolymer-coated adenovirus.Biomaterials. 2011 Dec;32(35):9536-45. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.069. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Biomaterials. 2011. PMID: 21959008 Free PMC article.
-
Design of smart HPMA copolymer-based nanomedicines.J Control Release. 2016 Oct 28;240:9-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.10.003. Epub 2015 Oct 3. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 26437260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering biodegradable and multifunctional peptide-based polymers for gene delivery.J Biol Eng. 2013 Oct 24;7(1):25. doi: 10.1186/1754-1611-7-25. J Biol Eng. 2013. PMID: 24156736 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of brush-like cationic copolymers for nonviral gene delivery.Biomacromolecules. 2013 Jan 14;14(1):275-84. doi: 10.1021/bm301747r. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Biomacromolecules. 2013. PMID: 23240866 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Ligands Deliver Model Drug Cargo into the Central Nervous System along Autonomic Neurons.ACS Nano. 2019 Oct 22;13(10):10961-10971. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b01515. Epub 2019 Oct 7. ACS Nano. 2019. PMID: 31589023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aubry S, Burlina F, Dupont E, Delaroche D, Joliot A, Lavielle S, Chassaing G, Sagan S. Cell-surface thiols affect cell entry of disulfide-conjugated peptides. FASEB J. 2009;23:2956–2967. - PubMed
-
- Bauhuber S, Hozsa C, Breunig M, Gopferich A. Delivery of Nucleic Acids via Disulfide-Based Carrier Systems. Advanced Materials. 2009;21:3286–3306. - PubMed
-
- Boeckle S, on Gersdorff C, van der Piepen S, Culmsee C, Wagner E, Ogris M. Purification of polyethylenimine polyplexes highlights the role of free polycations in gene transfer. Journal of Gene Medicine. 2004;6(10):1102–1111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

