Rac signaling in breast cancer: a tale of GEFs and GAPs
- PMID: 21893191
- PMCID: PMC3312797
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.08.011
Rac signaling in breast cancer: a tale of GEFs and GAPs
Abstract
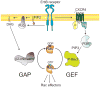
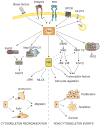
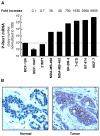
Rac GTPases, small G-proteins widely implicated in tumorigenesis and metastasis, transduce signals from tyrosine-kinase, G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), and integrins, and control a number of essential cellular functions including motility, adhesion, and proliferation. Deregulation of Rac signaling in cancer is generally a consequence of enhanced upstream inputs from tyrosine-kinase receptors, PI3K or Guanine nucleotide Exchange Factors (GEFs), or reduced Rac inactivation by GTPase Activating Proteins (GAPs). In breast cancer cells Rac1 is a downstream effector of ErbB receptors and mediates migratory responses by ErbB1/EGFR ligands such as EGF or TGFα and ErbB3 ligands such as heregulins. Recent advances in the field led to the identification of the Rac-GEF P-Rex1 as an essential mediator of Rac1 responses in breast cancer cells. P-Rex1 is activated by the PI3K product PIP3 and Gβγ subunits, and integrates signals from ErbB receptors and GPCRs. Most notably, P-Rex1 is highly overexpressed in human luminal breast tumors, particularly those expressing ErbB2 and estrogen receptor (ER). The P-Rex1/Rac signaling pathway may represent an attractive target for breast cancer therapy.
Copyright © 2011. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Manser E. Dev Cell. 2002;3(3):323–328. - PubMed
-
- Wennerberg K, Der CJ. J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt 8):1301–1312. - PubMed
-
- Del Pozo MA, Kiosses WB, Alderson NB, Meller N, Hahn KM, Schwartz MA. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4(3):232–239. - PubMed
-
- Price LS, Langeslag M, ten Klooster JP, Hordijk PL, Jalink K, Collard JG. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(41):39413–39421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

