Incidence of epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 21893672
- PMCID: PMC3171955
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31822cfc90
Incidence of epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To estimate the pooled incidence of epilepsy from published studies and investigate sources of heterogeneity in the estimates.
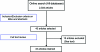
Methods: We searched online databases for incidence studies and used meta-analytic methods to analyze the data.
Results: Thirty-three articles met the entry criteria. The median incidence of epilepsy was 50.4/100,000/year (interquartile range [IQR] 33.6-75.6), while it was 45.0 (IQR 30.3-66.7) for high-income countries and 81.7 (IQR 28.0-239.5) for low- and middle-income countries. Population-based studies had higher incidence estimates than hospital-based studies (p = 0.02) while retrospective study design was associated with lower estimates than prospective studies (p = 0.04).
Conclusion: We provide data that could potentially be used to assess the burden and analyze the trends in incidence of epilepsy. Our results support the need for large population-based incidence studies of epilepsy.
References
-
- WHO Epilepsy in the WHO Africa Region: Bridging the Gap: The Global Campaign Against Epilepsy: “Out of the Shadows.” Geneva: WHO; 2004
-
- Sander JW. Some aspects of prognosis in the epilepsies: a review. Epilepsia 1993;34:1007–1016 - PubMed
-
- Carpio A, Bharucha NE, Jallon P, et al. Mortality of epilepsy in developing countries. Epilepsia 2005;46(suppl 11):28–32 - PubMed
-
- Diop AG, Hesdorffer DC, Logroscino G, Hauser WA. Epilepsy and mortality in Africa: a review of the literature. Epilepsia 2005;46(suppl 11):33–35 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous