Participatory and persuasive telehealth
- PMID: 21893945
- PMCID: PMC7077176
- DOI: 10.1159/000329892
Participatory and persuasive telehealth
Abstract
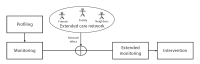
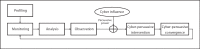
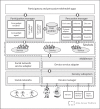
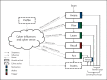
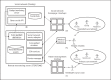
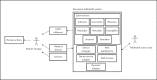
Technological advances in telehealth systems are primarily focused on sensing and monitoring. However, these systems are limited in that they only rely on sensors and medical devices to obtain vital signs. New research and development are urgently needed to offer more effective and meaningful interactions between patients, medical professionals and other individuals around the patients. Social networking with Web 2.0 technologies and methods can meet these demands, and help to develop a more complete view of the patient. Also many people, including the elderly, may be resistant to change, which can reduce the efficacy of telehealth systems. Persuasive technology and mechanisms are urgently needed to counter this resistance and promote healthy lifestyles. In this paper, we propose the participatory and persuasive telehealth system as a solution for these two limitations. By integrating connected health solutions with social networking and adding persuasive influence, we increase the chances for effective interventions and behavior alterations.
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

References
-
- Healthy Aging. Improving and Extending Quality of Life Among Older Americans: At a Glance 2009. http://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/resources/publications/AAG/aging.htm.
-
- Weitzel M, Smith A, Lee D, Deugd S, Helal S, Participatory medicine: leveraging social networks in telehealth solutions . Ambient Assistive Health and Wellness Management in the Heart of the City. In: Mokhtari M, Khalil I, Bauchet J, Zhang D, Nugent C, editors. Heidelberg, Springer. vol 5597. 2009. pp. pp 40–47.
-
- Lee D, Helal S, Johnson BD. An action-based behavior model for persuasive telehealth. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Smart Homes and Health Telematics (ICOST), Seoul. 2010 Jun
-
- Helal A, Bose R, Chen C, Smith A, de Deugd S, Cook D. STEPSTONE: a SODA case study in personal tele-health management. J Ambient Intell Smart Environ, submitted
-
- The Continua Health Alliance http://www.continuaalliance.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

