The biometric measurement of alcohol consumption
- PMID: 21895709
- PMCID: PMC3461278
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01605.x
The biometric measurement of alcohol consumption
Abstract
Background: Proper ascertainment of the history of alcohol consumption by an individual is an important component of medical diagnosis of disease and influences the implementation of appropriate treatment strategies that include prescription of medication, as well as intervention for the negative physical and social consequences of hazardous/harmful levels of alcohol consumption. Biological (biometric) diagnostic tests that provide information on current and past quantity and frequency of alcohol consumption by an individual, prior to onset of organ damage, continue to be sought.
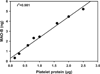
Methods: Platelet monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) protein was quantitated in 2 populations of subjects who had histories of different levels of alcohol consumption. Levels were assayed by immunoblotting or by ELISA. The development and evaluation of the new ELISA-based measure of platelet MAO-B protein levels is described.
Results: One subject population constituted a nontreatment-seeking, cross-sectional subject sample, and the other population was a longitudinally followed, hospitalized group of subjects. An algorithm combining measures of platelet MAO-B protein with the plasma levels of carbohydrate-deficient transferrin (CDT) and with liver enzymes (aspartate aminotransferase or γ-glutamyltransferase [GGT]) can detect hazardous/harmful alcohol use (HHAU) with the highest sensitivity and specificity in the cross-sectional nontreatment-seeking population. In the treatment-seeking population, low MAO-B protein levels at admission are associated with heavy drinking prior to admission, and these protein levels increase over a period of abstinence from alcohol.
Conclusions: The platelet MAO-B protein measurement is particularly effective for male alcohol consumers. The combined use of MAO-B protein measures together with measures of CDT and GGT does, however, improve the diagnostic utility of both markers for ascertaining HHAU in women. Furthermore, measurement of changes in platelet MAO-B protein levels during treatment for alcohol dependence may help monitor the success of the treatment program.
Copyright © 2011 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures



References
-
- Anthenelli RM, Tipp J, Li TK, Magnes L, Schuckit MA, Rice J, Daw W, Nurnberger JI., Jr Platelet monoamine oxidase activity in subgroups of alcoholics and controls: results from the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:598–604. - PubMed
-
- Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1986;51:1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Berlin I, Anthenelli RM. Monoamine oxidases and tobacco smoking. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2001;4:33–42. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Conigrave KM, Macaskill P, Whitfield JB, Irwig L. Combining carbohydrate-deficient transferrin and gamma-glutamyltransferase to increase diagnostic accuracy for problem drinking. Alcohol Alcohol. 2003;38:574–582. - PubMed
-
- Conigrave KM, Davies P, Haber P, Whitfield JB. Traditional markers of excessive alcohol use. Addiction. 2003;98(Suppl 2):31–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

