A cell factory of Bacillus subtilis engineered for the simple bioconversion of myo-inositol to scyllo-inositol, a potential therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 21896210
- PMCID: PMC3176187
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-10-69
A cell factory of Bacillus subtilis engineered for the simple bioconversion of myo-inositol to scyllo-inositol, a potential therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: A stereoisomer of inositol, scyllo-inositol, is known as a promising therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease, since it prevents the accumulation of beta-amyloid deposits, a hallmark of the disease. However, this compound is relatively rare in nature, whereas another stereoisomer of inositol, myo-inositol, is abundantly available.
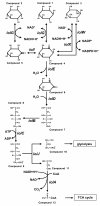
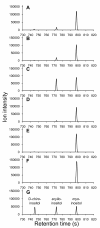
Results: Bacillus subtilis possesses a unique inositol metabolism involving both stereoisomers. We manipulated the inositol metabolism in B. subtilis to permit the possible bioconversion from myo-inositol to scyllo-inositol. Within 48 h of cultivation, the engineered strain was able to convert almost half of 10 g/L myo-inositol to scyllo-inositol that accumulated in the culture medium.
Conclusions: The engineered B. subtilis serves as a prototype of cell factory enabling a novel and inexpensive supply of scyllo-inositol.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An improved Bacillus subtilis cell factory for producing scyllo-inositol, a promising therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease.Microb Cell Fact. 2013 Dec 11;12:124. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-12-124. Microb Cell Fact. 2013. PMID: 24325193 Free PMC article.
-
A bacterial cell factory converting glucose into scyllo-inositol, a therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease.Commun Biol. 2020 Mar 2;3(1):93. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-0814-7. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 32123276 Free PMC article.
-
A new-generation of Bacillus subtilis cell factory for further elevated scyllo-inositol production.Microb Cell Fact. 2017 Apr 21;16(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0682-0. Microb Cell Fact. 2017. PMID: 28431560 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis and production of quercitols and their application in the production of pharmaceuticals: current status and prospects.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Jun;102(11):4641-4651. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8972-y. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29663050 Review.
-
Microbial synthesis of health-promoting inositols.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2024 Jun;87:103114. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2024.103114. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38520822 Review.
Cited by
-
Simple synthesis of 32P-labelled inositol hexakisphosphates for study of phosphate transformations.Plant Soil. 2018 Jun;427(1-2):149-161. doi: 10.1007/s11104-017-3315-9. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Plant Soil. 2018. PMID: 29880988 Free PMC article.
-
An improved Bacillus subtilis cell factory for producing scyllo-inositol, a promising therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease.Microb Cell Fact. 2013 Dec 11;12:124. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-12-124. Microb Cell Fact. 2013. PMID: 24325193 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic Relationships and Potential Functional Attributes of the Genus Parapedobacter: A Member of Family Sphingobacteriaceae.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 4;11:1725. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01725. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33013721 Free PMC article.
-
A bacterial cell factory converting glucose into scyllo-inositol, a therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease.Commun Biol. 2020 Mar 2;3(1):93. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-0814-7. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 32123276 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic regulation of metabolic flux in engineered bacteria using a pathway-independent quorum-sensing circuit.Nat Biotechnol. 2017 Mar;35(3):273-279. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3796. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Nat Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28191902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- What is Alzheimer's disease? http://www.alzheimers.org.uk/site/scripts/documents_info.php?documentID=100
-
- Irvine RF, Schell MJ. Back in the water: the return of the inositol phosphates. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:327–338. - PubMed
-
- Reddy NR, Sathe SK, Salunkhe DK. Phytates in legumes and cereals. Adv Food Res. 1982;28:1–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

