Towards non-surgical therapy for uterine fibroids: catechol-O-methyl transferase inhibitor shrinks uterine fibroid lesions in the Eker rat model
- PMID: 21896544
- PMCID: PMC3196875
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/der280
Towards non-surgical therapy for uterine fibroids: catechol-O-methyl transferase inhibitor shrinks uterine fibroid lesions in the Eker rat model
Abstract
Background: Uterine leiomyomas (fibroids) are the most common pelvic tumors in women. We assessed the potential therapeutic utility of Ro 41-0960, a synthetic catechol-O-methyl transferase inhibitor (COMTI), in the Eker rat.
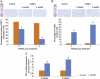
Methods: We randomized uterine fibroid-bearing Eker rats for treatment with Ro 41-0960 (150 mg/kg/12 h) versus vehicle for 2 and 4 weeks. The fibroids were measured by caliper and subjected to histological evaluation. Urinary levels of 2-hydroxy estrogen (E(2)), 16-hydroxy E2 and DPD (osteoporosis marker) and serum liver enzymes were evaluated. Expressions of Cyclin D1, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase1 (PARP1), tumor suppressor gene (P53) and transforming growth factor (TGFβ3) were assessed in fibroids using immunohistochemical analysis or RT-PCR. Apoptosis was confirmed using terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL).
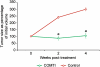
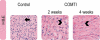
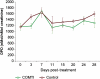
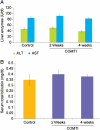
Results: Ro 41-0960-treated rats exhibited fibroid volumes of 86 ± 7% and 105 ± 12% of initial burden, at 2 and 4 weeks post-treatment, respectively, significantly lower than control group (240 ± 15% and 300 ± 18%; P< 0.01). Ro 41-0960 increased the urinary 2-hydroxy E2/16-hydroxy E(2) ratio, level of p53 mRNA and TUNEL positivity (P< 0.05) and decreased PARP1, PCNA and cyclin D1 proteins and TGFβ3 mRNA (P< 0.05). Ro 41-0960 did not change normal tissue histology, liver functions or urinary DPD level.
Conclusions: Ro 41-0960 (COMTI) arrested growth/shrunk uterine fibroids in Eker rats. This result may be related to modulation of estrogen-dependent genes involved in apoptosis, proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition via accumulation of 2-hydroxy estrogen. The efficacy and safety of Ro 41-0960 in rats suggest its candidacy for treatment of uterine fibroids.
Figures


References
-
- Acil Y, Brinckman J, Nothbohm H, Muller K, Batge B. Changes with age in the urinary excretion of hydroxylysylpyridinoline (HP) and lysylpyridinoline (LP) Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1996;56:275–283. doi:10.3109/00365519609088617. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahsan H, Chen Y, Whittemore AS, Kibriya MG, Gurvich I, Senie RT, Santella RM. A family-based genetic association study of variants in estrogen-metabolism genes COMT and CYP1B1 and breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004;85:121–131. doi:10.1023/B:BREA.0000025401.60794.68. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Hendy A, Salama S. Gene therapy and uterine leiomyoma: a review. Hum Reprod Update. 2006a;16:385–400. doi:10.1093/humupd/dml015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Hendy A, Salama SA. Ethnic distribution of estrogen receptor-alpha polymorphism is associated with a higher prevalence of uterine leiomyomas in black Americans. Fertil Steril. 2006b;86:686–693. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2006.01.052. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Hendy A, Lee EJ, Wang HQ, Copland JA. Gene therapy of uterine leiomyomas: adenovirus-mediated expression of dominant negative estrogen receptor inhibits tumor growth in nude mice. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;191:1621–1631. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2004.04.022. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

