Itraconazole inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 21896639
- PMCID: PMC3206167
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0691
Itraconazole inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
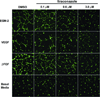
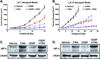
The antiangiogenic agent bevacizumab has been approved for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), although the survival benefit associated with this agent is marginal, and toxicities and cost are substantial. A recent screen for selective inhibitors of endothelial cell proliferation identified the oral antifungal drug itraconazole as a novel agent with potential antiangiogenic activity. In this article, we define and characterize the antiangiogenic and anticancer activities of itraconazole in relevant preclinical models of angiogenesis and lung cancer. Itraconazole consistently showed potent, specific, and dose-dependent inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation in response to both VEGF- and basic fibroblast growth factor-mediated angiogenic stimulation. In vivo, using primary xenograft models of human NSCLC, oral itraconazole showed single-agent growth-inhibitory activity associated with induction of tumor hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha expression and marked inhibition of tumor vascularity. Itraconazole significantly enhanced the antitumor efficacy of the chemotherapeutic agent cisplatin in the same model systems. Taken together, these data suggest that itraconazole has potent and selective inhibitory activity against multiple key aspects of tumor-associated angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo, and strongly support clinical translation of its use. Based on these observations, we have initiated a randomized phase II study comparing the efficacy of standard cytotoxic therapy with or without daily oral itraconazole in patients with recurrent metastatic NSCLC.
©2011 AACR.
Figures



References
-
- Folkman J. Tumor Angiogenesis: Therapeutic Implications. N Engl J Med. 1971;285:1182–1186. - PubMed
-
- Niki T, Iba S, Tokunou M, Yamada T, Matsuno Y, Hirohashi S. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factors A, B, C, and D and their relationships to lymph node status in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:2431–2439. - PubMed
-
- Han H, Silverman J, Santucci T, Macherey RS, dAmato TA, Tung MY, et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Correlates With Neoangiogenesis and a Poor Prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001;8:72–79. - PubMed
-
- Bremnes RM, Camps C, Sirera R. Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: The prognostic impact of neoangiogenesis and the cytokines VEGF and bFGF in tumours and blood. Lung Cancer. 2006;51:143–158. - PubMed
-
- Asahara T, Bauters C, Zheng LP, Takeshita S, Bunting S, Ferrara N, et al. Synergistic effect of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor on angiogenesis in vivo. Circulation. 1995;92:365–371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

