Amino acid substitution in NPC1 that abolishes cholesterol binding reproduces phenotype of complete NPC1 deficiency in mice
- PMID: 21896731
- PMCID: PMC3174677
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1112751108
Amino acid substitution in NPC1 that abolishes cholesterol binding reproduces phenotype of complete NPC1 deficiency in mice
Abstract
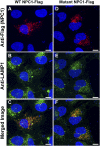
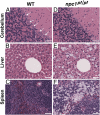
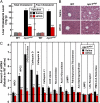
Substitution mutations in adjacent amino acids of the N-terminal domain of NPC1, a lysosomal membrane protein, abolish its cholesterol binding activity and impair its ability to export cholesterol from lysosomes of cultured cells lacking npc1 [Kwon HJ, et al. (2009) Cell 137:1213-1224]. Here, we show that the same two mutations (proline-202 and phenylalanine-203, both changed to alanine) reproduce the phenotype of complete NPC1 deficiency when knocked into the mouse npc1 gene by homologous recombination. Homozygous npc1(pf/pf) mice exhibited neurodegeneration beginning at day 49 and died at a median age of 84 d, as previously reported for mice that lack npc1. Liver and other organs of the npc1(pf/pf) mice accumulated excess cholesterol in lysosomes. In liver, mRNAs encoding several lysosomal proteins were elevated, including NPC1 and NPC2 and several digestive enzymes (acid lipase, β-glucuronidase, and cathepsins B and D). Weekly treatment with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPCD) beginning at 7 wk reduced hepatic cholesterol accumulation and diminished the lysosomal mRNAs. We conclude that the cholesterol binding site in the N-terminal domain of NPC1 is essential for cholesterol export from lysosomes in living animals as it is in cultured cells. The HPCD-mediated reduction of excess lysosomal enzymes may contribute to the ability of this drug to delay the progression of NPC disease in mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



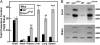
References
-
- Pentchev PG, Vanier MT, Suzuki K, Patterson MC. In: The Metabolic and Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease. Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1995. pp. 2625–2639.
-
- Infante RE, et al. Purified NPC1 protein: II. Localization of sterol binding to a 240-amino acid soluble luminal loop. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:1064–1075. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

