Medial prefrontal cortex and striatum mediate the influence of social comparison on the decision process
- PMID: 21896760
- PMCID: PMC3179055
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1100892108
Medial prefrontal cortex and striatum mediate the influence of social comparison on the decision process
Abstract
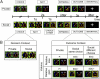
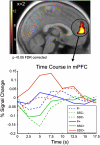
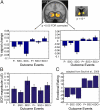
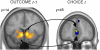
We compared private and social decision making to investigate the neural underpinnings of the effect of social comparison on risky choices. We measured brain activity using functional MRI while participants chose between two lotteries: in the private condition, they observed the outcome of the unchosen lottery, and in the social condition, the outcome of the lottery chosen by another person. The striatum, a reward-related brain structure, showed higher activity when participants won more than their counterpart (social gains) compared with winning in isolation and lower activity when they won less than their counterpart (social loss) compared with private loss. The medial prefrontal cortex, implicated in social reasoning, was more activated by social gains than all other events. Sensitivity to social gains influenced both brain activity and behavior during subsequent choices. Specifically, striatal activity associated with social gains predicted medial prefrontal cortex activity during social choices, and experienced social gains induced more risky and competitive behavior in later trials. These results show that interplay between reward and social reasoning networks mediates the influence of social comparison on the decision process.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bell DE. Regret in decision making under uncertainty. Oper Res. 1982;30:961–981.
-
- Loomes G, Sugden R. Regret theory: An alternative theory of rational choice under uncertainty. Econ J. 1982;92:805–824.
-
- Ritov I. Probability of regret: Anticipation of uncertainty resolution in choice. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process. 1996;66:228–236.
-
- Zeelenberg M, Beattie J, van der Pligt J, de Vries NK. Consequences of regret aversion: Effects of expected feedback on risky decision making. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process. 1996;65:148–158.
-
- Coricelli G, Rustichini A. Reward-based emotions: Affective evaluation of outcomes and regret learning. In: Tremblay L, Dreher JC, editors. Handbook of Reward and Decision Making. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2009. pp. 427–439.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

