Social ecological analysis of an outbreak of pufferfish egg poisoning in a coastal area of Bangladesh
- PMID: 21896811
- PMCID: PMC3163873
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.2011.10-0629
Social ecological analysis of an outbreak of pufferfish egg poisoning in a coastal area of Bangladesh
Abstract
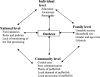
Recurrent outbreaks of marine pufferfish poisoning in Bangladesh highlight the need to understand the context in which the outbreaks occurred. In a recent outbreak investigation, a multidisciplinary team conducted a mixed-method study to identify the demography and clinical manifestation of the victims and to explore different uses of pufferfish, and local buying, selling, and processing practices. The outbreak primarily affected a low income household where an elderly woman collected and cooked pufferfish egg curry. Nine persons consumed the curry, and symptoms developed in 6 (67%) of these persons. Symptoms included vomiting, diarrhea, paresis, and tingling sensation; 2 (22%) persons died. The unstable income of the affected family, food crisis, and the public disposal of unsafe pufferfish byproducts all contributed to the outbreak. A multi-level intervention should be developed and disseminated with the participation of target communities to discourage unsafe discarding of pufferfish scraps and to improve the community knowledge about the risk of consuming pufferfish.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: None of the authors have any conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Diener M, Christian B, Ahmed MS, Luckas B. Determination of tetrodotoxin and its analogs in the puffer fish Takifugu oblongus from Bangladesh by hydrophilic interaction chromatography and mass-spectrometric detection. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;389:1997–2002. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed S. Puffer fish tragedy in Bangladesh: an incident of Takifugu oblongus poisoning in Degholia, Khulna. Afr J Mar Sci. 2006;28:457–458.
-
- Mahmud Y, Tanu MB, Noguchi T. First occurrence of a food poisoning incident due to ingestion of Takifugu oblongus, along with a toxicological report on three marine puffer species in Bangladesh. J Food Hyg Soc Japan. 1999;40:473–480.
-
- Islam QT, Razzak MA, Islam MA, Bari MI, Basher A, Chowdhury FR, Sayeduzzaman AB, Ahasan HA, Faiz MA, Arakawa O, Yotsu-Yamashita M, Kuch U, Mebs D. Puffer fish poisoning in Bangladesh: clinical and toxicological results from large outbreaks in 2008. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2010;105:74–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical