Model to predict mortality in critically ill adults with acute kidney injury
- PMID: 21896828
- PMCID: PMC3359007
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.02900311
Model to predict mortality in critically ill adults with acute kidney injury
Abstract
Background and objectives: Acute kidney injury (AKI) requiring dialysis is associated with high mortality. Most prognostic tools used to describe case complexity and to project patient outcome lack predictive accuracy when applied in patients with AKI. In this study, we developed an AKI-specific predictive model for 60-day mortality and compared the model to the performance of two generic (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment [SOFA] and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II [APACHE II]) scores, and a disease specific (Cleveland Clinic [CCF]) score.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Data from 1122 subjects enrolled in the Veterans Affairs/National Institutes of Health Acute Renal Failure Trial Network study; a multicenter randomized trial of intensive versus less intensive renal support in critically ill patients with AKI conducted between November 2003 and July 2007 at 27 VA- and university-affiliated centers.
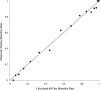
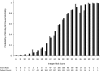
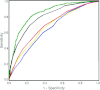
Results: The 60-day mortality was 53%. Twenty-one independent predictors of 60-day mortality were identified. The logistic regression model exhibited good discrimination, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of 0.85 (0.83 to 0.88), and a derived integer risk score yielded a value of 0.80 (0.77 to 0.83). Existing scoring systems, including APACHE II, SOFA, and CCF, when applied to our cohort, showed relatively poor discrimination, reflected by areas under the ROC curve of 0.68 (0.64 to 0.71), 0.69 (0.66 to 0.73), and 0.65 (0.62 to 0.69), respectively.
Conclusions: Our new risk model outperformed existing generic and disease-specific scoring systems in predicting 60-day mortality in critically ill patients with AKI. The current model requires external validation before it can be applied to other patient populations.
Figures
References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, Ronco C: Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: A multinational, multicenter study. J Am Med Assoc 294: 813–818, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bagshaw SM, Berthiaume LR, Delaney A, Bellomo R: Continuous versus intermittent renal replacement therapy for critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: A meta-analysis. Crit Care Med 36: 610–617, 2008 - PubMed
-
- VA/NIH Acute Renal Failure Trial Network, Palevsky PM, Zhang JH, O'Connor TZ, Chertow GM, Crowley ST, Choudhury D, Finkel K, Kellum JA, Paganini E, Schein RM, Smith MW, Swanson KM, Thompson BT, Vijayan A, Watnick S, Star RA, Peduzzi P: Intensity of renal support in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med 359: 7–20, 2008 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

