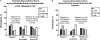Cardiovascular disease among hispanics and non-hispanics in the chronic renal insufficiency cohort (CRIC) study
- PMID: 21896829
- PMCID: PMC3359008
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.11341210
Cardiovascular disease among hispanics and non-hispanics in the chronic renal insufficiency cohort (CRIC) study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Hispanics are the largest minority group in the United States. The leading cause of death in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is cardiovascular disease (CVD), yet little is known about its prevalence among Hispanics with CKD.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We conducted cross-sectional analyses of prevalent self-reported clinical and subclinical measures of CVD among 497 Hispanics, 1638 non-Hispanic Caucasians, and 1650 non-Hispanic African Americans, aged 21 to 74 years, with mild-to-moderate CKD at enrollment in the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) and Hispanic CRIC (HCRIC) studies. Measures of subclinical CVD included left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), coronary artery calcification (CAC), and ankle-brachial index.
Results: Self-reported coronary heart disease (CHD) was lower in Hispanics compared with non-Hispanic Caucasians (18% versus 23%, P = 0.02). Compared with non-Hispanic Caucasians, Hispanics had a lower prevalence of CAC >100 (41% versus 34%, P = 0.03) and CAC >400 (26% versus 19%, P = 0.02). However, after adjusting for sociodemographic factors, these differences were no longer significant. In adjusted analyses, Hispanics had a higher odds of LVH compared with non-Hispanic Caucasians (odds ratio 1.97, 95% confidence interval, 1.22 to 3.17, P = 0.005), and a higher odds of CAC >400 compared with non-Hispanic African Americans (odds ratio, 2.49, 95% confidence interval, 1.11 to 5.58, P = 0.03). Hispanic ethnicity was not independently associated with any other CVD measures.
Conclusions: Prevalent LVH was more common among Hispanics than non-Hispanic Caucasians, and elevated CAC score was more common among Hispanics than non-Hispanic African Americans. Understanding reasons for these racial/ethnic differences and their association with long-term clinical outcomes is needed.
Figures
References
-
- US Census Bureau Hispanic Heritage Month 2010: Sept 15-Oct 15. US Census Bureau Newsroom Web site. http://www.census.gov/newsroom/releases/archives/facts_for_features_spec... Accessed March 1, 2011
-
- U.S. Renal Data System, USRDS 2010 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda MD, 2010
-
- Weiner DE, Tighiouart H, Amin MG, Stark PC, MacLeod B, Griffith JL, Salem DN, Levey AS, Sarnak MJ: Chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality: A pooled analysis of community-based studies. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 1307–1315, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351: 1296–1305, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Culleton BF, Larson MG, Wilson PW, Evans JC, Parfrey PS, Levy D: Cardiovascular disease and mortality in a community-based cohort with mild renal insufficiency. Kidney Int 56: 2214–2219, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK002651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK062234/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR-000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK60980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072231/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR-013987-06/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK072231/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR013987/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR005096/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR-05096/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR-16500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5K24DK002651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK06102/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases