Test-retest, within-visit variability of Goldmann visual fields in retinitis pigmentosa
- PMID: 21896857
- PMCID: PMC3208001
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.11-8321
Test-retest, within-visit variability of Goldmann visual fields in retinitis pigmentosa
Abstract
Purpose: Reliable outcome measures are needed to estimate changes in peripheral vision during future treatment clinical trials for retinal degeneration patients. The authors examined the short-term variability of Goldmann visual field (GVF) results converted to retinal areas in retinitis pigmentosa (RP) subjects.
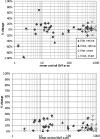
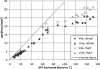
Methods: Two within-visit GVFs were obtained from one eye each of 37 RP subjects with visual acuity better than 20/400 by a single experienced operator using the V4e (n = 28) or III4e (n = 12) target, or both. Planimetric GVF measures were digitized and converted to retinal areas in square millimeters by a single independent user. The 95% coefficient of repeatability (CR.(95)) for percentage change in central retinal area was determined from the test-retest difference.
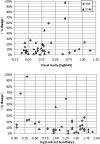
Results: There were no significant systematic trends toward either increase or decrease between the first and second GVF. For the III4e target, the CR.(95) was 23.7% on average across all 12 subjects. For the V4e target, the CR.(95) was 32.8% on average across all 28 subjects. However, 3 of 8 subjects with a geometric mean retinal area <10 mm(2) (∼7° radius) for the V4e target exhibited unusually large variability (50%-100%), and the CR.(95) was 19.2% when these three subjects were excluded. Variability was not statistically significantly related to visual acuity, age, presence of cystoid macular edema, or subjects' stress or anxiety levels.
Conclusions: Inherent test-retest variability (CR.(95)) of functional retinal areas derived from GVF results in a clinical RP population can be limited to <20% by using a single experienced operator, making the GVF the measure of choice for changes in peripheral vision.
Figures
References
-
- Schatz A, Röck T, Naycheva L, et al. Transcorneal electrical stimulation for patients with retinitis pigmentosa: a prospective, randomized, sham-controlled exploratory study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(7):4485–4496 - PubMed
-
- Ross DF, Fishman GA, Gilbert LD, Anderson RJ. Variability of visual field measurements in normal subjects and patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984;102(7):1004–1010 - PubMed
-
- Berson EL, Sandberg MA, Rosner B, Birch DG, Hanson AH. Natural course of retinitis pigmentosa over a three-year interval. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985;99(3):240–251 - PubMed
-
- Seiple W, Clemens CJ, Greenstein VC, et al. Test-retest reliability of the multifocal electroretinogram and Humphrey visual fields in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Doc Ophthalmol. 2004;109(3):255–272 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

