Overexpression of the sodium chloride cotransporter is not sufficient to cause familial hyperkalemic hypertension
- PMID: 21896937
- PMCID: PMC3199361
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.167809
Overexpression of the sodium chloride cotransporter is not sufficient to cause familial hyperkalemic hypertension
Abstract
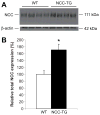
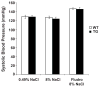
The sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC) is the primary target of thiazides diuretics, drugs used commonly for long-term hypertension therapy. Thiazides also completely reverse the signs of familial hyperkalemic hypertension (FHHt), suggesting that the primary defect in FHHt is increased NCC activity. To test whether increased NCC abundance alone is sufficient to generate the FHHt phenotype, we generated NCC transgenic mice; surprisingly, these mice did not display an FHHt-like phenotype. Systolic blood pressures of NCC transgenic mice did not differ from those of wild-type mice, even after dietary salt loading. NCC transgenic mice also did not display hyperkalemia or hypercalciuria, even when challenged with dietary electrolyte manipulation. Administration of fludrocortisone to NCC transgenic mice, to stimulate NCC, resulted in an increase in systolic blood pressure equivalent to that of wild-type mice (approximately 20 mm Hg). Although total NCC abundance was increased in the transgenic animals, phosphorylated (activated) NCC was not, suggesting that the defect in FHHt involves either activation of ion transport pathways other than NCC, or else direct activation of NCC, in addition to an increase in NCC abundance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
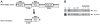
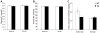
References
-
- Farfel Z, Iaina A, Rosenthal T, Waks U, Shibolet S, Gafni J. Familial hyperpotassemia and hypertension accompanied by normal plasma aldosterone levels: Possible hereditary cell membrane defect. Arch Intern Med. 1978;138:1828–1832. - PubMed
-
- Wilson FH, Disse-Nicodeme S, Choate KA, Ishikawa K, Nelson-Williams C, Desitter I, Gunel M, Milford DV, Lipkin GW, Achard JM, Feely MP, Dussol B, Berland Y, Unwin RJ, Mayan H, Simon DB, Farfel Z, Jeunemaitre X, Lifton RP. Human hypertension caused by mutations in wnk kinases. Science. 2001;293:1107–1112. - PubMed
-
- Achard JM, Disse-Nicodeme S, Fiquet-Kempf B, Jeunemaitre X. Phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity of familial hyperkalaemic hypertension (gordon syndrome) Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001;28:1048–1052. - PubMed
-
- Mayan H, Vered I, Mouallem M, Tzadok-Witkon M, Pauzner R, Farfel Z. Pseudohypoaldosteronism type ii: Marked sensitivity to thiazides, hypercalciuria, normomagnesemia, and low bone mineral density. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:3248–3254. - PubMed
-
- Xu B, English JM, Wilsbacher JL, Stippec S, Goldsmith EJ, Cobb MH. Wnk1, a novel mammalian serine/threonine protein kinase lacking the catalytic lysine in subdomain ii. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:16795–16801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

