Signal and noise properties of position-sensitive avalanche photodiodes
- PMID: 21896961
- PMCID: PMC3180891
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/56/19/011
Signal and noise properties of position-sensitive avalanche photodiodes
Abstract
After many years of development, position-sensitive avalanche photodiodes (PSAPDs) are now being incorporated into a range of scintillation detector systems, including those used in high-resolution small-animal PET and PET/MR scanners. In this work, the signal, noise, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), flood histogram and timing resolution were measured for lutetium oxyorthosilicate (LSO) scintillator arrays coupled to PSAPDs ranging in size from 10 to 20 mm, and the optimum bias voltage and working temperature were determined. Variations in the SNR performance of PSAPDs with the same dimensions were small, but the SNR decreased significantly with increasing PSAPD size and increasing temperature. Smaller PSAPDs (10 mm and 15 mm in width) produced acceptable flood histograms at 24 °C, and cooling lower than 16 °C produced little improvement. The optimum bias voltage was about 25 V below the break down voltage. The larger 20 mm PSAPDs have lower SNR and require cooling to 0-7 °C for acceptable performance. The optimum bias voltage is also lower (35 V or more below the break down voltage depending on the temperature). Significant changes in the timing resolution were observed as the bias voltage and temperature varied. Higher bias voltages provided better timing resolution. The best timing resolution obtained for individual crystals was 2.8 ns and 3.3 ns for the 10 mm and 15 mm PSAPDs, respectively. The results of this work provide useful guidance for selecting the bias voltage and working temperature for scintillation detectors that incorporate PSAPDs as the photodetector.
Figures

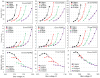
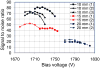



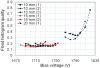
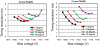
References
-
- Bergeron M, Cadorette J, Beaudoin JF, Lepage MD, Robert G, Selivanov V, Tetrault MA, Viscogliosi N, Norenberg JP, Fontaine R, Lecomte R. Performance evaluation of the LabPET APD-based digital PET scanner. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2009;56:10–6.
-
- Burr KC, Ivan A, Castleberry DE, LeBlanc JW, Shah KS, Farrell R. Evaluation of a prototype small animal PET detector with depth-of-interaction encoding. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2004;51:1791–8.
-
- Casey ME, Reynolds C, Binkley DM, Rochelle JM. Analysis of timing performance for an APD-LSO scintillation detector. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A-Accel Spectrom Dect Assoc Equip. 2003;504:143–8.
-
- Catana C, Wu YB, Judenhofer MS, Qi JY, Pichler BJ, Cherry SR. Simultaneous acquisition of multislice PET and MR images: Initial results with a MR-compatible PET scanner. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:1968–76. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhari AJ, Yang YF, Farrell R, Dokhale PA, Shah KS, Cherry SR, Badawi RD. PSPMT/APD hybrid DOI detectors for the PET component of a dedicated breast PET/CT system - A feasibility study. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2008;55:853–61.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
