Evaluation of glycoproteins purified from adult and larval camel ticks (Hyalomma dromedarii) as a candidate vaccine
- PMID: 21897098
- PMCID: PMC3165153
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2011.12.3.243
Evaluation of glycoproteins purified from adult and larval camel ticks (Hyalomma dromedarii) as a candidate vaccine
Abstract
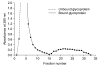
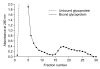
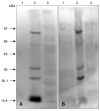
In order to identify antigens that can help prevent camel tick infestations, three major glycoproteins (GLPs) about 97, 66 and 40 kDa in size were purified from adult and larval Egyptian ticks, Hyalomma (H.) dromedarii, using a single-step purification method with Con-A sepharose. The purified GLPs were evaluated as vaccines against camel tick infestation in rabbits. The rabbits received three intramuscular inoculations of GLPs (20 µg/animal) on days 0, 14, and 28. In the immunoblot analysis, Sera from the immunized rabbits recognized the native GLPs and other proteins from larval and adult H. dromedarii ticks along with those from other tick species such as Rhipicephalus sanguineus but not Ornithodoros moubata. The effects of immunity induced by these GLPs were determined by exposing rabbits to adult H. dromedarii ticks. These results demonstrated that GLP immunization led to a slightly decreased reproductive index and significantly reduced rates of egg hatchability. These results demonstrated that immunization with the purified GLPs can provide protection against infestation by H. dromedarii and some other tick species. Further studies are needed to confirm the effectiveness of immunization with GLPs against other tick species.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Purification and characterization of two larval glycoproteins from the cattle tick, Boophilus annulatus.J Vet Sci. 2007 Jun;8(2):175-80. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2007.8.2.175. J Vet Sci. 2007. PMID: 17519572 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of vaccine candidates purified from the adult ticks of Ornithodoros savignyi (Acari: Argasidae) and Hyalomma dromedarii (Acari: Ixodidae) against tick infestations.J Parasit Dis. 2019 Jun;43(2):246-255. doi: 10.1007/s12639-018-01082-3. Epub 2019 Jan 18. J Parasit Dis. 2019. PMID: 31263330 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial immunization of rabbits with Hyalomma dromedarii tick-derived midgut antigen.Exp Appl Acarol. 1995 Jun;19(6):319-24. doi: 10.1007/BF00052389. Exp Appl Acarol. 1995. PMID: 8521745
-
Issues in tick vaccine development: identification and characterization of potential candidate vaccine antigens.Microbes Infect. 2000 Sep;2(11):1353-61. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(00)01289-2. Microbes Infect. 2000. PMID: 11018452 Review.
-
Advances in the identification and characterization of protective antigens for recombinant vaccines against tick infestations.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2003 Aug;2(4):583-93. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2.4.583. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2003. PMID: 14711342 Review.
Cited by
-
Mining the secreted and membrane transcriptome of Hyalomma dromedarii ticks for identification of potential protective antigens.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Nov 11;17(1):462. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06538-5. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 39529157 Free PMC article.
-
A review on Hyalomma species infestations on human and animals and progress on management strategies.Heliyon. 2020 Dec 9;6(12):e05675. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05675. eCollection 2020 Dec. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33319114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The control of Hyalomma ticks, vectors of the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus: Where are we now and where are we going?PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022 Nov 17;16(11):e0010846. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010846. eCollection 2022 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022. PMID: 36395110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photosensitizers in the fight against ticks: safranin as a novel photodynamic fluorescent acaricide to control the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii (Ixodidae).Parasitol Res. 2016 Oct;115(10):3747-58. doi: 10.1007/s00436-016-5136-9. Epub 2016 May 27. Parasitol Res. 2016. PMID: 27230018
-
Transmission-Blocking Vaccines: Focus on Anti-Vector Vaccines against Tick-Borne Diseases.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2015 Jun;63(3):169-79. doi: 10.1007/s00005-014-0324-8. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2015. PMID: 25503555 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Shafy S, Mahmoud MS, Abdel-Aziz MM. Evaluation of crude and fractionated gut extract antigens for protection against camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii (Acari: Ixodidae) J Entomol. 2008;5:91–102.
-
- Allen JR, Humphreys SJ. Immunisation of guinea pigs and cattle against ticks. Nature. 1979;280:491–493. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JF. The natural history of ticks. Med Clin North Am. 2002;86:205–218. - PubMed
-
- Apanaskevich DA, Schuster AL, Horak IG. The Genus Hyalomma: VII. Redescription of all Parasitic Stages of H. (Euhyalomma) dromedarii and H. E. schulzei (Acari: Ixodidae) J Med Entomol. 2008;45:817–831. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

