Importance of associative learning processes for one-trial behavioral sensitization of preweanling rats
- PMID: 21897205
- PMCID: PMC3174322
- DOI: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e32834affb2
Importance of associative learning processes for one-trial behavioral sensitization of preweanling rats
Abstract
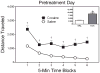
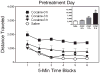
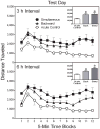
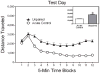
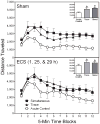
During adulthood, associative learning is necessary for the expression of one-trial behavioral sensitization; however, it is uncertain whether the same associative processes are operative during the preweanling period. Two strategies were used to assess the importance of associative learning for one-trial behavioral sensitization of preweanling rats. In the initial experiments, we varied both the sequence and time interval between presentation of the conditioned stimulus (CS, novel environment) and unconditioned stimulus (US, cocaine). In the final experiment, we determined whether electroconvulsive shock-induced retrograde amnesia would disrupt one-trial behavioral sensitization. Results showed that robust-sensitized responding was apparent regardless of the sequence in which cocaine and the novel environment (the presumptive CS) were presented. Varying the time between CS and US presentation (0, 3, or 6 h) was also without effect. Results from experiment 3 showed that single or multiple electroconvulsive shock treatments did not alter the expression of the sensitized response. Therefore, these data indicated that one-trial behavioral sensitization of preweanling rats was exclusively mediated by nonassociative mechanisms and that associative processes did not modulate sensitized responding. These findings are in contrast to what is observed during adulthood, as adult rats exhibit one-trial behavioral sensitization only when associative processes are operative.
Figures


References
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Robinson TE. Sensitization to the psychomotor stimulant effects of amphetamine: modulation by associative learning. Behav Neurosci. 1996;110:1397–1414. - PubMed
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Schallert T, Robinson TE. Memory processes governing amphetamine-induced psychomotor sensitization. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;26:703–715. - PubMed
-
- Andrade C, Thyagarajan S, Vinod PS, Srikanth SN, Rao NS, Chandra JS. Effect of stimulus intensity and number of treatments on ECS-related seizure duration and retrograde amnesia in rats. J ECT. 2002;18:197–202. - PubMed
-
- Andrade C, Singh NM, Thyagarajan S, Nagaraja N, Rao NSK, Chandra JS. Possible glutamatergic and lipid signalling mechanisms in ECT-induced retrograde amnesia: experimental evidence for involvement of COX-2, and review of literature. J Psychiatr Res. 2008;42:837–850. - PubMed
-
- Ayres JJB, Haddad C, Albert M. One-trial excitatory backward conditioning as assessed by suppression of licking in rats: concurrent observation of lick suppression and defensive behaviors. Anim Learn Behav. 1987;15:212–217.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

