Epigenetic silencing of the oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster during PU.1-directed macrophage differentiation
- PMID: 21897363
- PMCID: PMC3230374
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.317
Epigenetic silencing of the oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster during PU.1-directed macrophage differentiation
Abstract
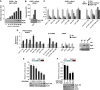
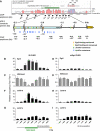
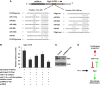
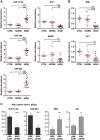
The oncogenic cluster miR-17-92 encodes seven related microRNAs that regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis and development. Expression of miR-17-92 cluster is decreased upon cell differentiation. Here, we report a novel mechanism of the regulation of miR-17-92 cluster. Using transgenic PU.1(-/-) myeloid progenitors we show that upon macrophage differentiation, the transcription factor PU.1 induces the secondary determinant Egr2 which, in turn, directly represses miR-17-92 expression by recruiting histone demethylase Jarid1b leading to histone H3 lysine K4 demethylation within the CpG island at the miR-17-92 promoter. Conversely, Egr2 itself is targeted by miR-17-92, indicating existence of mutual regulatory relationship between miR-17-92 and Egr2. Furthermore, restoring EGR2 levels in primary acute myeloid leukaemia blasts expressing elevated levels of miR-17-92 and low levels of PU.1 and EGR2 leads to downregulation of miR-17-92 and restored expression of its targets p21CIP1 and BIM. We propose that upon macrophage differentiation PU.1 represses the miR-17-92 cluster promoter by an Egr-2/Jarid1b-mediated H3K4 demethylation mechanism whose deregulation may contribute to leukaemic states.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Jumonji/ARID1 B (JARID1B) protein promotes breast tumor cell cycle progression through epigenetic repression of microRNA let-7e.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 25;286(47):40531-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.304865. Epub 2011 Oct 3. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21969366 Free PMC article.
-
MIR-23A microRNA cluster inhibits B-cell development.Exp Hematol. 2010 Aug;38(8):629-640.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.04.004. Epub 2010 May 5. Exp Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20399246 Free PMC article.
-
The PU.1-Modulated MicroRNA-22 Is a Regulator of Monocyte/Macrophage Differentiation and Acute Myeloid Leukemia.PLoS Genet. 2016 Sep 12;12(9):e1006259. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006259. eCollection 2016 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27617961 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell fate specification: role of master regulatory switch transcription factor PU.1 in differential hematopoiesis.Stem Cells Dev. 2005 Apr;14(2):140-52. doi: 10.1089/scd.2005.14.140. Stem Cells Dev. 2005. PMID: 15910240 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs as Regulators of Phagocytosis.Cells. 2022 Apr 19;11(9):1380. doi: 10.3390/cells11091380. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EpimiR: a database of curated mutual regulation between miRNAs and epigenetic modifications.Database (Oxford). 2014 Mar 28;2014:bau023. doi: 10.1093/database/bau023. Print 2014. Database (Oxford). 2014. PMID: 24682734 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-17-92 and miR-221/222 cluster members target KIT and ETV1 in human gastrointestinal stromal tumours.Br J Cancer. 2013 Sep 17;109(6):1625-35. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.483. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23969726 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Dysfunction Under Diabetic Conditions by miR-504.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 May;36(5):864-73. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306770. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26941017 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs and piRNAs from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles induce cell survival and inhibit cell differentiation of cord blood hematopoietic stem cells: a new insight in transplantation.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 9;7(6):6676-92. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6791. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26760763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Back J, Dierich A, Bronn C, Kastner P, Chan S (2004) PU.1 determines the self-renewal capacity of erythroid progenitor cells. Blood 103: 3615–3623 - PubMed
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, Zhao K (2007) High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 129: 823–837 - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Kamal M, Lindblad-Toh K, Bekiranov S, Bailey DK, Huebert DJ, McMahon S, Karlsson EK, Kulbokas EJ 3rd, Gingeras TR, Schreiber SL, Lander ES (2005) Genomic maps and comparative analysis of histone modifications in human and mouse. Cell 120: 169–181 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

