A pathophysiological framework of hippocampal dysfunction in ageing and disease
- PMID: 21897434
- PMCID: PMC3312472
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn3085
A pathophysiological framework of hippocampal dysfunction in ageing and disease
Abstract
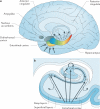
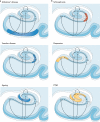
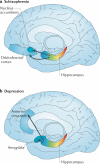
The hippocampal formation has been implicated in a growing number of disorders, from Alzheimer's disease and cognitive ageing to schizophrenia and depression. How can the hippocampal formation, a complex circuit that spans the temporal lobes, be involved in a range of such phenotypically diverse and mechanistically distinct disorders? Recent neuroimaging findings indicate that these disorders differentially target distinct subregions of the hippocampal circuit. In addition, some disorders are associated with hippocampal hypometabolism, whereas others show evidence of hypermetabolism. Interpreted in the context of the functional and molecular organization of the hippocampal circuit, these observations give rise to a unified pathophysiological framework of hippocampal dysfunction.
Figures

Comment in
-
Imaging hippocampal subregions with in vivo MRI: advances and limitations.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011 Dec 20;13(1):70. doi: 10.1038/nrn3085-c1. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22183437 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sloviter RS, Sollas AL, Dean E, Neubort S. Adrenalectomy-induced granule cell degeneration in the rat hippocampal dentate gyrus: characterization of an in vivo model of controlled neuronal death. J. Comp. Neurol. 1993;330:324–336. - PubMed
-
- Zhao X, et al. Transcriptional profiling reveals strict boundaries between hippocampal subregions. J. Comp. Neurol. 2001;441:187–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG035015/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG003376/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG025161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH090563/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AG035015/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23MH09056/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG034618/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG034618/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG003376/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH093398/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AG003376/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH093398/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036722/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

