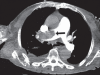
Massive pulmonary embolism and cardio-pulmonary resuscitation leading to disseminated intravascular coagulation
- PMID: 21897613
- PMCID: PMC3159264
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-6247.83266
Massive pulmonary embolism and cardio-pulmonary resuscitation leading to disseminated intravascular coagulation
Figures
Similar articles
-
Massive pulmonary embolism presenting as disseminated intravascular coagulation.Hawaii Med J. 1992 May;51(5):121, 125, 134. Hawaii Med J. 1992. PMID: 1601644
-
Pulmonary embolism presenting as disseminated intravascular coagulation.Hong Kong Med J. 2002 Apr;8(2):142-3. Hong Kong Med J. 2002. PMID: 11937670
-
Unrecognized pulmonary embolism presenting as disseminated intravascular coagulation.Am J Med. 1984 May;76(5):772-8. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90985-9. Am J Med. 1984. PMID: 6720724
-
Hematologic Emergencies in the Postoperative Neurointensive Care Unit Setting: Illustrative Case Series and Differential Diagnosis.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021 Oct;30(10):106019. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.106019. Epub 2021 Aug 3. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021. PMID: 34359018 Review.
-
COVID-19 coagulopathy: is it disseminated intravascular coagulation?Intern Emerg Med. 2021 Mar;16(2):309-312. doi: 10.1007/s11739-020-02601-y. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Intern Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33368021 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pesola GR, Carlon GC. Pulmonary embolus induced disseminated intravascular coagulation. Crit Care Med. 1987;15:983–4. - PubMed
-
- Choi SS, Pang SY, Mak WP, Ko A. Pulmonary embolism presenting as disseminated intravascular coagulation. Hong Kong Med J. 2002;8:142–3. - PubMed
-
- Leitner JM, Jilma B, Spiel AO, Sterz F, Laggner AN, Janata KM. Massive pulmonary embolism leading to cardiac arrest is associated with consumptive coagulopathy presenting as disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8:1477–82. - PubMed
-
- McKay DG, Franciosi R, Zeller J. Symposium on thrombohemorrhagic phenomenon. II. Am J Cardiol. 1967;20:374–80. - PubMed
-
- Yuan SM, Shinfeld A, Tager S, Raanani E. Aortic aneurysm-induced disseminated intravascular coagulopathy: Successful surgical repair. Vascular. 2009;17:55–9. - PubMed