Evaluation of antioxidant potential of Amalakayas Rasayana: A polyherbal Ayurvedic formulation
- PMID: 21897639
- PMCID: PMC3157105
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-7788.83186
Evaluation of antioxidant potential of Amalakayas Rasayana: A polyherbal Ayurvedic formulation
Abstract
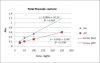
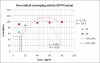
Amalakayas Rasayana (AR) is a polyherbal formulation mentioned in Ayurveda to treat aging and age-associated diseases. Being an antiaging drug, AR may have antioxidants and free radical scavenging activity to minimize free radical-induced damage which is a key cause of aging. The methanolic extract of AR was evaluated in vitro for total phenolic and tannin content, free radical scavenging activity, superoxide radical scavenging activity, and reducing power. The total phenolic content was measured using Folin-ciocalteu reagent against gallic acid [relative standard deviation (R(2)) = 0.998]. Total tannin was estimated using the Stephen method and was found to be 2.82% w/w. Free radical scavenging activity was measured by 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl hydrazyl assay and R(2) was 1. Superoxide radical scavenging activity was done by ethylene diamine tetra acetate and Nitro Blue Tetrazolium Chloride assays against ascorbic acid and R(2) was 0.976 (EC(50)= 77.5 μg/ml). Ferrous reducing power was evaluated by Oyaizu method where R(2) was 0.986. All studies showed that AR possesses antioxidant activity. The results of this study suggest that the antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of AR may explain its rasayana effect and justify its use as a medicine for age associated diseases.
Keywords: Amalakayas Rasayana; Antioxidant; DPPH; anti-radical; reducing power.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Braca A, Sortino C, Politi M, Morelli I, Mendez J. Antioxidant Activity of flavonoids from Licania licaniaeflora. J Ethnopharmacol. 2002;79:379–81. - PubMed
-
- Maxwell SR. Prospects for the use of antioxidant therapies. Drugs. 1995;49:345–61. - PubMed
-
- Niki E, Shimaski H, Mino M. Antioxidantism-free radical and biological defense. Tokyo: Gakkai Syuppn Centre; 1994. pp. 3–16.
-
- Shasthri K, Chaturvedi G. Charaka Samhita with Vidyotini Commentoty. Varanasi: Chaukambha Bharati Academy; 2007. pp. 35–6.
-
- Yadavji Trikamji Acharya. Charaka Samhita. Varanasi: Chaukambha Prakashan; 2009. p. 377.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
