Human immunodeficiency virus and liver disease forum 2010: conference proceedings
- PMID: 21898501
- PMCID: PMC3795389
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.24651
Human immunodeficiency virus and liver disease forum 2010: conference proceedings
Abstract
Liver disease continues to represent a critical mediator of morbidity and mortality in those with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. The frequent presence and overlap of concomitant injurious processes, including hepatitis C virus and hepatitis B virus infections, hepatoxicity associated with antiretroviral therapeutic agents, alcohol, and other toxins, in the setting of immunosuppression lead to rapid fibrotic progression and early development of end-stage liver disease. This conference summary describes the proceedings of a state-of-the-art gathering of international experts designed to highlight the status of current research in epidemiology, natural history, pathogenesis, and treatment of HIV and liver disease.
Copyright © 2011 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Unrestricted educational grants from pharmaceutical sponsors to support this meeting were provided by Genentech, Inc., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Merck & Co., Three Rivers Pharmaceuticals, LLC, and Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Continuing Medical Education credit and content oversight were provided by Medical Education Resources, Inc. Dr. Sherman advises and received grants from Merck, Vertex, SciClone, and Roche. He advises Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Baxter, and Regulus. He received grants from Gilead, Boehringer Ingelheim, Siemens, and Anadys. He holds other interests with Pfizer, Tibotec, and Medpace.
Figures

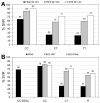
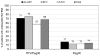
References
-
- Salmon-Ceron D, Rosenthal E, Lewden C, Bouteloup V, May T, Burty C, et al. Emerging role of hepatocellular carcinoma among liver-related causes of deaths in HIV-infected patients: the French national Mortalite 2005 study. J Hepatol. 2009;50:736–745. - PubMed
-
- Macías J, Berenguer J, Japón MA, Girón JA, Rivero A, López-Cortés LF, et al. Fast fibrosis progression between repeated liver biopsies in patients coinfected with human immunodeficiency virus/hepatitis C virus. Hepatology. 2009;50:1056–1063. - PubMed
-
- Sulkowski MS, Mehta SH, Torbenson MS, Higgins Y, Brinkley SC, de Oca RM, et al. Rapid fibrosis progression among HIV/hepatitis C virus-co-infected adults. AIDS. 2007;21:2209–2216. - PubMed
-
- Bräu N, Salvatore M, Ríos-Bedoya CF, Fernández-Carbia A, Paronetto F, Rodríguez-Orengo JF, et al. Slower fibrosis progression in HIV/ HCV-coinfected patients with successful HIV suppression using antiretroviral therapy. J Hepatol. 2006;44:47–55. - PubMed
-
- Pineda JA, Aguilar-Guisado M, Rivero A, Girón-González JA, Ruiz-Morales J, Merino D, et al. Natural history of compensated hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis in HIV-infected patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:1274–1282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
