Surviving the sun: repair and bypass of DNA UV lesions
- PMID: 21898645
- PMCID: PMC3267942
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.723
Surviving the sun: repair and bypass of DNA UV lesions
Abstract
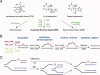
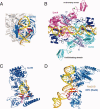
Structural studies of UV-induced lesions and their complexes with repair proteins reveal an intrinsic flexibility of DNA at lesion sites. Reduced DNA rigidity stems primarily from the loss of base stacking, which may manifest as bending, unwinding, base unstacking, or flipping out. The intrinsic flexibility at UV lesions allows efficient initial lesion recognition within a pool of millions to billions of normal DNA base pairs. To bypass the damaged site by translesion synthesis, the specialized DNA polymerase η acts like a molecular "splint" and reinforces B-form DNA by numerous protein-phosphate interactions. Photolyases and glycosylases that specifically repair UV lesions interact directly with UV lesions in bent DNA via surface complementation. UvrA and UvrB, which recognize a variety of lesions in the bacterial nucleotide excision repair pathway, appear to exploit hysteresis exhibited by DNA lesions and conduct an ATP-dependent stress test to distort and separate DNA strands. Similar stress tests are likely conducted in eukaryotic nucleotide excision repair.
Copyright © 2011 The Protein Society.
Figures
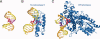


References
-
- Friedberg EC, Walker GC, Siede W, Wood RD, Schultz RA, Ellenberger T. DNA repair and mutagenesis. 2nd ed. Washington: DC: ASM Press; 2006.
-
- Sancar A. Structure and function of DNA photolyase and cryptochrome blue-light photoreceptors. Chem Rev. 2003;103:2203–2237. - PubMed
-
- Latham KA, Lloyd RS. T4 endonuclease V. Perspectives on catalysis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1994;726:181–196. discussion 196–187. - PubMed
-
- Goosen N, Moolenaar GF. Repair of UV damage in bacteria. DNA Repair (Amst) 2008;7:353–379. - PubMed
-
- Kaur B, Doetsch PW. Ultraviolet damage endonuclease (Uve1p): a structure and strand-specific DNA endonuclease. Biochemistry. 2000;39:5788–5796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

