Crystallographic snapshots of tyrosine phenol-lyase show that substrate strain plays a role in C-C bond cleavage
- PMID: 21899319
- PMCID: PMC3191766
- DOI: 10.1021/ja203361g
Crystallographic snapshots of tyrosine phenol-lyase show that substrate strain plays a role in C-C bond cleavage
Abstract
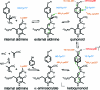
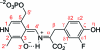
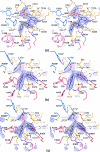
The key step in the enzymatic reaction catalyzed by tyrosine phenol-lyase (TPL) is reversible cleavage of the Cβ-Cγ bond of L-tyrosine. Here, we present X-ray structures for two enzymatic states that form just before and after the cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond. As for most other pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent enzymes, the first state, a quinonoid intermediate, is central for the catalysis. We captured this relatively unstable intermediate in the crystalline state by introducing substitutions Y71F or F448H in Citrobacter freundii TPL and briefly soaking crystals of the mutant enzymes with a substrate 3-fluoro-L-tyrosine followed by flash-cooling. The X-ray structures, determined at ~2.0 Å resolution, reveal two quinonoid geometries: "relaxed" in the open and "tense" in the closed state of the active site. The "tense" state is characterized by changes in enzyme contacts made with the substrate's phenolic moiety, which result in significantly strained conformation at Cβ and Cγ positions. We also captured, at 2.25 Å resolution, the X-ray structure for the state just after the substrate's Cβ-Cγ bond cleavage by preparing the ternary complex between TPL, alanine quinonoid and pyridine N-oxide, which mimics the α-aminoacrylate intermediate with bound phenol. In this state, the enzyme-ligand contacts remain almost exactly the same as in the "tense" quinonoid, indicating that the strain induced by the closure of the active site facilitates elimination of phenol. Taken together, structural observations demonstrate that the enzyme serves not only to stabilize the transition state but also to destabilize the ground state.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The role of substrate strain in the mechanism of the carbon-carbon lyases.Bioorg Chem. 2014 Dec;57:198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 28. Bioorg Chem. 2014. PMID: 25035301 Review.
-
Crystal Structures of Wild-Type and F448A Mutant Citrobacter freundii Tyrosine Phenol-Lyase Complexed with a Substrate and Inhibitors: Implications for the Reaction Mechanism.Biochemistry. 2018 Oct 30;57(43):6166-6179. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00724. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 30260636
-
Citrobacter freundii tyrosine phenol-lyase: the role of asparagine 185 in modulating enzyme function through stabilization of a quinonoid intermediate.Protein Eng. 2000 Mar;13(3):207-15. doi: 10.1093/protein/13.3.207. Protein Eng. 2000. PMID: 10775663
-
Insights into the catalytic mechanism of tyrosine phenol-lyase from X-ray structures of quinonoid intermediates.J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 24;283(43):29206-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802061200. Epub 2008 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18715865 Free PMC article.
-
Chemistry and diversity of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate dependent enzymes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Sep;1854(9):1167-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.12.028. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25615531 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficient strategies to enhance plasmid stability for fermentation of recombinant Escherichia coli harboring tyrosine phenol lyase.Biotechnol Lett. 2021 Jul;43(7):1265-1276. doi: 10.1007/s10529-021-03082-5. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Biotechnol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33830386
-
M379A Mutant Tyrosine Phenol-lyase from Citrobacter freundii Has Altered Conformational Dynamics.Chembiochem. 2022 Jul 5;23(13):e202200028. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202200028. Epub 2022 May 24. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 35577764 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid production of l-DOPA by Vibrio natriegens, an emerging next-generation whole-cell catalysis chassis.Microb Biotechnol. 2022 May;15(5):1610-1621. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14001. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Microb Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35006649 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of enzymes with new specificity by high-throughput screening using DmpR-based genetic circuits and multiple flow cytometry rounds.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 8;8(1):2659. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20943-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29422524 Free PMC article.
-
Research overview of L-DOPA production using a bacterial enzyme, tyrosine phenol-lyase.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2023;99(3):75-101. doi: 10.2183/pjab.99.006. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36908174 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kumagai H.; Yamada H.; Matsui H.; Ohkishi H.; Ogata K. J. Biol. Chem. 1970, 245, 1767–1772. - PubMed
- Phillips R. S. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1987, 256, 302–310. - PubMed
- Enei H.; Nakazawa H.; Matsui H.; Okumura S.; Yamada H. FEBS Lett. 1972, 21, 39–41. - PubMed
- Yamada H.; Kumagai H. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 19, 249–288. - PubMed
- Yamada H.; Kumagai H.; Kashima N.; Torii H.; Enei H.; Okumura S. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1972, 46, 370–374. - PubMed
- Kim K.; Cole P. A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 1205–1208. - PubMed
- Faleev N. G.; Zhukov Y. N.; Khurs E. N.; Gogoleva O. I.; Barbolina M. V.; Bazhulina N. P.; Belikov V. M.; Demidkina T. V.; Khomutov R. M. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 6897–6902. - PubMed
-
- Kumagai H.; Matsui H.; Ohgishi H.; Ogata K.; Yamada H.; Ueno T.; Fukami H. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1969, 34, 266–270. - PubMed
- Ueno T.; Fukami H.; Ohkishi H.; Kumagai H.; Yamada H. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1970, 206, 476–479. - PubMed
- Phillips R. S.; Ravichandran K.; Von Tersch R. L. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1989, 11, 80–83.
- Watkins E. B.; Phillips R. S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 2099–2100. - PubMed
- Lee S.-G.; Ro H.-S.; Hong S.-P.; Kim E.-H.; Sung M.-H. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 6, 98–102.
-
- Mouratou B.; Kasper P.; Gehring H.; Christen P. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1320–1325. - PubMed
- Seisser B.; Zinkl R.; Gruber K.; Kaufmann F.; Hafner A.; Kroutil W. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 731–736.
- Kim J. H.; Song J. J.; Kim B. G.; Sung M. H.; Lee S. C. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 14, 153–157.
- Lee S.-G.; Hong S.-P.; Kim D. Y.; Song J. J.; Ro H.-S.; Sung M.-H. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 5564–5573. - PubMed
- Rha E.; Kim S.; Choi S. L.; Hong S. P.; Sung M. H.; Song J. J.; Lee S. G. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 6187–6194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

