Differential expression of interleukin-32 in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps
- PMID: 21899560
- PMCID: PMC3235261
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02706.x
Differential expression of interleukin-32 in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps
Abstract
Background: Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a heterogeneous disease characterized by local inflammation of the upper airways and sinuses and is frequently divided into polypoid CRS (CRSwNP) and nonpolypoid CRS (CRSsNP). However, the mechanism of inflammation in CRS has still not been fully elucidated. The aim of the study was to investigate the role of interleukin-32 (IL-32), a recently discovered proinflammatory cytokine, in CRS.
Methods: We collected nasal epithelial cells and nasal tissue from patients with CRS and control subjects. We assayed mRNA for IL-32 by real-time PCR and measured IL-32 protein using ELISA, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry.
Results: The expression of mRNA for IL-32 was elevated in epithelial cells from uncinate tissue from patients with CRSsNP compared with patients with CRSwNP (P < 0.05), control subjects (P=0.06), and epithelial cells from nasal polyp (NP) tissue (P < 0.05). Production of IL-32 was induced by IFN-γ, TNF, and dsRNA in primary airway epithelial cells. In whole-tissue extracts, the expression of IL-32 protein was significantly elevated in patients with CRSwNP compared with patients with CRSsNP and control subjects. Immunohistochemistry data showed that IL-32 was detected in mucosal epithelial cells and inflammatory cells in the lamina propria. Levels of IL-32 were correlated with the levels of CD3 and macrophage mannose receptor in NP tissue. Immunofluorescence data showed IL-32 co-localization with CD3-positive T cells and CD68-positive macrophages in NPs.
Conclusion: Overproduction of IL-32 may be involved in the pathogenesis of CRS, although the role of IL-32 in the inflammation in CRSsNP and CRSwNP may be different.
© 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures

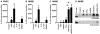
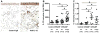


References
-
- Benninger MS, Ferguson BJ, Hadley JA, Hamilos DL, Jacobs M, Kennedy DW, et al. Adult chronic rhinosinusitis: definitions, diagnosis, epidemiology, and pathophysiology. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;129(3 Suppl):S1–32. - PubMed
-
- Banerji A, Piccirillo JF, Thawley SE, Levitt RG, Schechtman KB, Kramper MA, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis patients with polyps or polypoid mucosa have a greater burden of illness. Am J Rhinol. 2007;21(1):19–26. - PubMed
-
- Van Zele T, Claeys S, Gevaert P, Van Maele G, Holtappels G, Van Cauwenberge P, et al. Differentiation of chronic sinus diseases by measurement of inflammatory mediators. Allergy. 2006;61(11):1280–1289. - PubMed
-
- Bachert C, Van Bruaene N, Toskala E, Zhang N, Olze H, Scadding G, et al. Important research questions in allergy and related diseases: 3-chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis - a GALEN study. Allergy. 2009;64(4):520–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

