MAPK/AP-1 activation mediates TLR2 agonist-induced SPLUNC1 expression in human lung epithelial cells
- PMID: 21899893
- PMCID: PMC3224182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2011.08.005
MAPK/AP-1 activation mediates TLR2 agonist-induced SPLUNC1 expression in human lung epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: Short Palate Lung and Nasal epithelium Clone 1 (SPLUNC1) is a newly described host defense protein, primarily expressed in large airway epithelial cells. Reduced SPLUNC1 has been reported in allergic and cigarette smoke-exposed airways. We found that Mycoplasma pneumoniae increases SPLUNC1 in airway epithelium in part via activating TLR2-NF-κB pathway. However, the contribution of additional signaling pathways to TLR2-mediated SPLUNC1 expression remains unclear. In the present study, we investigated if TLR2-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/activator protein-1 (AP-1) signaling regulates SPLUNC1 expression in human lung epithelial cells.
Methods: Human lung epithelial NCI-H292 cells were stimulated with a TLR2 agonist Palmitoyl (3)-Cys-Ser-Lys (4)-OH (Pam(3)CSK(4)). MAPK/AP-1 activation and its role in SPLUNC1 regulation were investigated by Western blot, c-Jun activation assay, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and real-time PCR. SPLUNC1 promoter activity was assessed by a luciferase reporter assay.
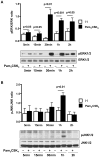
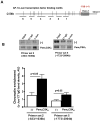
Results: Pam(3)CSK(4) increased SPLUNC1 expression in NCI-H292 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner, and enhanced SPLUNC1 promoter activity. Pam(3)CSK(4)-treated cells demonstrated activated MAPK and c-Jun compared to untreated cells. ChIP assay indicated increased c-Jun binding to the SPLUNC1 promoter following Pam(3)CSK(4) stimulation. Inhibition of ERK1/2 significantly reduced Pam(3)CSK(4)-mediated c-Jun activation and SPLUNC1 expression.
Conclusions: Our results for the first time demonstrate that TLR2-mediated MAPK/AP-1 activation up-regulates lung epithelial SPLUNC1 expression at the transcriptional level. Understanding SPLUNC1 gene regulation should provide more specific therapeutic targets to restore deficient SPLUNC1 production in diseased airways.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures







References
-
- Adiseshaiah P, Kalvakolanu DV, Reddy SP. A JNK-independent signaling pathway regulates TNF alpha-stimulated, c-Jun-driven FRA-1 protooncogene transcription in pulmonary epithelial cells. J Immunol. 2006;177:7193–7202. - PubMed
-
- Ballif BA, Blenis J. Molecular mechanisms mediating mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK cell survival signals. Cell Growth Differ. 2001;12:397–408. - PubMed
-
- Bingle CD, Bingle L. Characterisation of the human plunc gene, a gene product with an upper airways and nasopharyngeal restricted expression pattern. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1493:363–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

