Detection and characterization of a distinct bornavirus lineage from healthy Canada geese (Branta canadensis)
- PMID: 21900161
- PMCID: PMC3209299
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.05700-11
Detection and characterization of a distinct bornavirus lineage from healthy Canada geese (Branta canadensis)
Abstract
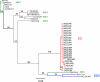
Avian bornaviruses (ABV), identified in 2008, infect captive parrots and macaws worldwide. The natural reservoirs of these viruses are unknown. Reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) was used to screen oropharyngeal/cloacal swab and brain samples from wild Canada geese (Branta canadensis) for ABV. Approximately 2.9% of swab samples were positive for bornavirus sequences. Fifty-two percent of brain samples from 2 urban flocks also tested positive, and brain isolates were cultured in duck embryo fibroblasts. Phylogenetic analyses placed goose isolates in an independent cluster, and more notably, important regulatory sequences present in Borna disease virus but lacking in psittacine ABVs were present in goose isolates.
Figures

References
-
- Daoust P. Y., Julian R. J., Yason C. V., Artsob H. 1991. Proventricular impaction associated with nonsuppurative encephalomyelitis and ganglioneuritis in 2 Canada geese. J. Wildl. Dis. 27: 513–517 - PubMed
-
- Delnatte P., et al. 2011. New genotype of avian bornavirus in wild geese and trumpeter swans in Canada. Vet. Rec. 169: 108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

