β-Actin specifically controls cell growth, migration, and the G-actin pool
- PMID: 21900491
- PMCID: PMC3204067
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-06-0582
β-Actin specifically controls cell growth, migration, and the G-actin pool
Abstract
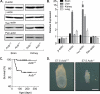
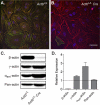
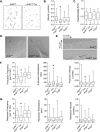
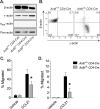
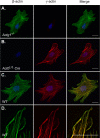
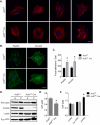
Ubiquitously expressed β-actin and γ-actin isoforms play critical roles in most cellular processes; however, their unique contributions are not well understood. We generated whole-body β-actin-knockout (Actb(-/-)) mice and demonstrated that β-actin is required for early embryonic development. Lethality of Actb(-/-) embryos correlated with severe growth impairment and migration defects in β-actin-knockout primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) that were not observed in γ-actin-null MEFs. Migration defects were associated with reduced membrane protrusion dynamics and increased focal adhesions. We also identified migration defects upon conditional ablation of β-actin in highly motile T cells. Of great interest, ablation of β-actin altered the ratio of globular actin (G-actin) to filamentous actin in MEFs, with corresponding changes in expression of genes that regulate the cell cycle and motility. These data support an essential role for β-actin in regulating cell migration and gene expression through control of the cellular G-actin pool.
Figures
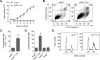
References
-
- Dugina V, Zwaenepoel I, Gabbiani G, Clement S, Chaponnier C. Beta and gamma-cytoplasmic actins display distinct distribution and functional diversity. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:2980–2988. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

