NADPH oxidase complex and IBD candidate gene studies: identification of a rare variant in NCF2 that results in reduced binding to RAC2
- PMID: 21900546
- PMCID: PMC3806486
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300078
NADPH oxidase complex and IBD candidate gene studies: identification of a rare variant in NCF2 that results in reduced binding to RAC2
Erratum in
- Gut. 2013 Oct;62(10):1432
Abstract
Objective: The NOX2 NADPH oxidase complex produces reactive oxygen species and plays a critical role in the killing of microbes by phagocytes. Genetic mutations in genes encoding components of the complex result in both X-linked and autosomal recessive forms of chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). Patients with CGD often develop intestinal inflammation that is histologically similar to Crohn's colitis, suggesting a common aetiology for both diseases. The aim of this study is to determine if polymorphisms in NOX2 NADPH oxidase complex genes that do not cause CGD are associated with the development of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Methods: Direct sequencing and candidate gene approaches were used to identify susceptibility loci in NADPH oxidase complex genes. Functional studies were carried out on identified variants. Novel findings were replicated in independent cohorts.
Results: Sequence analysis identified a novel missense variant in the neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 (NCF2) gene that is associated with very early onset IBD (VEO-IBD) and subsequently found in 4% of patients with VEO-IBD compared with 0.2% of controls (p=1.3×10(-5), OR 23.8 (95% CI 3.9 to 142.5); Fisher exact test). This variant reduced binding of the NCF2 gene product p67(phox) to RAC2. This study found a novel genetic association of RAC2 with Crohn's disease (CD) and replicated the previously reported association of NCF4 with ileal CD.
Conclusion: These studies suggest that the rare novel p67(phox) variant results in partial inhibition of oxidase function and are associated with CD in a subgroup of patients with VEO-IBD; and suggest that components of the NADPH oxidase complex are associated with CD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
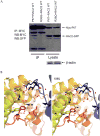
Comment in
-
Linking risk conferring mutations in NCF4 to functional consequences in Crohn's disease.Gut. 2012 Jul;61(7):1097; author reply 1097-8. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301344. Epub 2011 Oct 24. Gut. 2012. PMID: 22027479 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MOP97756/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- G0800675/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CZB/4/540/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- ETM/137/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- DK062420/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G1002033/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DK-06-2423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062420/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0600329/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 072789/Z/03/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0800759/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ETM/75/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
