Vulnerability to depression: from brain neuroplasticity to identification of biomarkers
- PMID: 21900567
- PMCID: PMC6623387
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1309-11.2011
Vulnerability to depression: from brain neuroplasticity to identification of biomarkers
Abstract
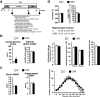
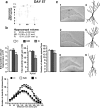
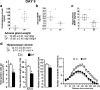
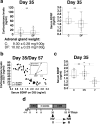
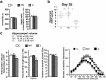
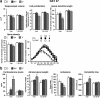
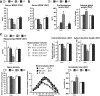
A stressful event increases the risk of developing depression later in life, but the possible predisposing factors remain unknown. Our study aims to characterize latent vulnerability traits underlying the development of depressive disorders in adult animals. Four weeks after a priming stressful event, serum corticosterone concentration returned to control values in all animals, whereas the other biological parameters returned to basal level in only 58% of animals (called nonvulnerable). In contrast, 42% of animals displayed persistent decreased serum and hippocampus BDNF concentrations, reduced hippocampal volume and neurogenesis, CA3 dendritic retraction and decrease in spine density, as well as amygdala neuron hypertrophy, constituting latent vulnerability traits to depression. In this group, called vulnerable, a subsequent mild stress evoked a rise of serum corticosterone levels and a "depressive" phenotype, in contrast to nonvulnerable animals. Intracerebroventricular administration of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, a selective TrkB receptor agonist, dampened the development of the "depressive" phenotype. Our results thus characterize the presence of latent vulnerability traits that underlie the emergence of depression and identify the association of low BDNF with normal corticosterone serum concentrations as a predictive biomarker of vulnerability to depression.
Figures


References
-
- Alleva E, Francia N. Psychiatric vulnerability: suggestions from animal models and role of neurotrophins. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2009;33:525–536. - PubMed
-
- Becker C, Zeau B, Rivat C, Blugeot A, Hamon M, Benoliel JJ. Repeated social defeat-induced depression-like behavioral and biological alterations in rats: involvement of cholecystokinin. Mol Psychiatry. 2008;13:1079–1092. - PubMed
-
- Bielajew C, Konkle AT, Merali Z. The effects of chronic mild stress on male Sprague-Dawley and Long Evans rats: I. Biochemical and physiological analyses. Behav Brain Res. 2002;136:583–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
