Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guidelines for CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotypes and warfarin dosing
- PMID: 21900891
- PMCID: PMC3187550
- DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2011.185
Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guidelines for CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotypes and warfarin dosing
Abstract
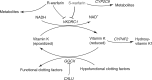
Warfarin is a widely used anticoagulant with a narrow therapeutic index and large interpatient variability in the dose required to achieve target anticoagulation. Common genetic variants in the cytochrome P450-2C9 (CYP2C9) and vitamin K-epoxide reductase complex (VKORC1) enzymes, in addition to known nongenetic factors, account for ~50% of warfarin dose variability. The purpose of this article is to assist in the interpretation and use of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotype data for estimating therapeutic warfarin dose to achieve an INR of 2-3, should genotype results be available to the clinician. The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) of the National Institutes of Health Pharmacogenomics Research Network develops peer-reviewed gene-drug guidelines that are published and updated periodically on http://www.pharmgkb.org based on new developments in the field.(1).
Figures

References
-
- Ansell J, Hirsh J, Hylek E, Jacobson A, Crowther M, Palareti G. American College of Chest Physicians. Pharmacology and management of the vitamin K antagonists: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. (8th Edition) 2008;133:160S–198S. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs LG. Warfarin pharmacology, clinical management, and evaluation of hemorrhagic risk for the elderly. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2006;22:17–32. vii. - PubMed
-
- Rieder MJ, et al. Effect of VKORC1 haplotypes on transcriptional regulation and warfarin dose. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;352:2285–2293. - PubMed
-
- Higashi MK, et al. Association between CYP2C9 genetic variants and anticoagulation-related outcomes during warfarin therapy. JAMA. 2002;287:1690–1698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

