BRCA1 tumour suppression occurs via heterochromatin-mediated silencing
- PMID: 21901007
- PMCID: PMC3240576
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10371
BRCA1 tumour suppression occurs via heterochromatin-mediated silencing
Abstract
Mutations in the tumour suppressor gene BRCA1 lead to breast and/or ovarian cancer. Here we show that loss of Brca1 in mice results in transcriptional de-repression of the tandemly repeated satellite DNA. Brca1 deficiency is accompanied by a reduction of condensed DNA regions in the genome and loss of ubiquitylation of histone H2A at satellite repeats. BRCA1 binds to satellite DNA regions and ubiquitylates H2A in vivo. Ectopic expression of H2A fused to ubiquitin reverses the effects of BRCA1 loss, indicating that BRCA1 maintains heterochromatin structure via ubiquitylation of histone H2A. Satellite DNA de-repression was also observed in mouse and human BRCA1-deficient breast cancers. Ectopic expression of satellite DNA can phenocopy BRCA1 loss in centrosome amplification, cell-cycle checkpoint defects, DNA damage and genomic instability. We propose that the role of BRCA1 in maintaining global heterochromatin integrity accounts for many of its tumour suppressor functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
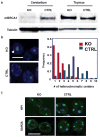
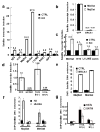
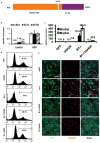
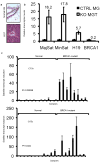
Comment in
-
Cancer: Let sleeping DNA lie.Nature. 2011 Sep 7;477(7363):169-70. doi: 10.1038/477169a. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21901006 No abstract available.
-
Tumour suppressors: Silencing heterochromatin.Nat Rev Cancer. 2011 Sep 29;11(11):760. doi: 10.1038/nrc3152. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21956483 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tutt A, Ashworth A. The relationship between the roles of BRCA1 genes in DNA repair and cancer predisposition. Trends in Molec Med. 2002;8:571–576. - PubMed
-
- King MC, Marks JH, Mandell JB. Breast and ovarian cancer risks due to inherited mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. Science. 2003;302(5645):643–646. - PubMed
-
- Pageau GJ, Hall LL, Ganesan S, Livingston DM, Lawrence JB. The disappearing Barr body in breast and ovarian cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(8):628–633. - PubMed
-
- Lane TF, et al. Expression of Brca1 is associated with terminal differentiation of ectodermally and mesodermally derived tissues in mice. Genes Dev. 1995;9:2712–2722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

