Effect of live Salmonella Ty21a in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis
- PMID: 21901076
- PMCID: PMC3155226
- DOI: 10.4137/dti.s220
Effect of live Salmonella Ty21a in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis
Abstract
Background: Intestinal microbiota seems to play an essential role in the development of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). We hypothesised that an oral vaccine based on live Salmonella typhi would be well tolerated and could even attenuate dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) induced colitis in rats, an animal model of IBD.
Methods: Nine male Wistar rats was used for an initial tolerance study, in which we used 3 dose-levels of Salmonella Ty21a, 0.5 × 10(9), 1 × 10(9), and 2 × 10(9)CFU, each dose being tested in 3 rats. Four treatment groups consisting of 8 male Wistar rats per group: 1) control group given standard food and water, 2) control group given four daily administrations of Salmonella Ty21a 1 × 10(9) CFU, 3) water with 5% DSS the last 7 days, 4) four daily administrations of Salmonella Ty21a before water with 5% DSS the last 7 days. The Salmonella Ty21a was administered by gastric gavage on day 1, 3, 5 and 16, while DSS was given with the drinking water from day 15 to 22. The animals were sacrificed and colonic tissue removed for analysis 22 days after gavage of the first vaccine dose.
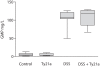
Results: The animals in the tolerance study got no signs of disease. In the treatment study, all animals receiving DSS had histologic indications of colitis, particularly in the distal part of the colon. Administration of Salmonella Ty21a had no significant effect on crypt and inflammation scores (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Gastric administration of live vaccine strain Salmonella Ty21a was well tolerated, but did not provide any significant protection against development of DSS induced colitis in rats.
Keywords: colitis; inflammatory bowel disease; rats; salmonella Ty21a.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Beneficial effects of live and dead Salmonella-based vector strain on the course of colitis in mice.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016 Nov;63(5):340-346. doi: 10.1111/lam.12632. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27501439
-
Kefir treatment ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Dec 14;21(46):13020-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i46.13020. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26676086 Free PMC article.
-
Fermented barley and soybean (BS) mixture enhances intestinal barrier function in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis mouse model.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Dec 3;16(1):498. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1479-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27912750 Free PMC article.
-
A murine colitis model developed using a combination of dextran sulfate sodium and Citrobacter rodentium.J Microbiol. 2018 Apr;56(4):272-279. doi: 10.1007/s12275-018-7504-x. Epub 2018 Apr 2. J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29611140 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose oral ferrous fumarate aggravated intestinal inflammation in rats with DSS-induced colitis.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2005 Aug;11(8):744-8. doi: 10.1097/01.mib.0000174374.83601.86. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2005. PMID: 16043990
References
-
- Bibiloni R, Fedorak RN, Tannock GW, Madsen KL, Gionchetti P, Campieri M, De Simone C, Sartor RB. VSL#3 probiotic-mixture induces remission in patients with active ulcerative colitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005;100(7):1539–46. - PubMed
-
- Boirivant M, Fuss IJ, Ferroni L, De Pascale M, Strober W. Oral administration of recombinant cholera toxin subunit B inhibits IL-12-mediated murine experimental (trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid) colitis. J. Immunol. 2001;166(5):3522–32. - PubMed
-
- Carrier J, Aghdassi E, Platt I, Cullen J, Allard JP. Effect of oral iron supplementation on oxidative stress and colonic inflammation in rats with induced colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001;15(12):1989–99. - PubMed
-
- Di Giacinto C, Marinaro M, Sanchez M, Strober W, Boirivant M. Probiotics ameliorate recurrent Th1-mediated murine colitis by inducing IL-10 and IL-10-dependent TGF-beta-bearing regulatory cells. J. Immunol. 2005;174(6):3237–46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

