Regulation of Caenorhabditis elegans p53/CEP-1-dependent germ cell apoptosis by Ras/MAPK signaling
- PMID: 21901106
- PMCID: PMC3161941
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002238
Regulation of Caenorhabditis elegans p53/CEP-1-dependent germ cell apoptosis by Ras/MAPK signaling
Abstract
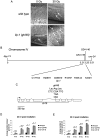
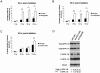
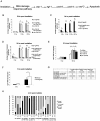
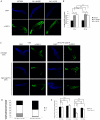
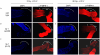
Maintaining genome stability in the germline is thought to be an evolutionarily ancient role of the p53 family. The sole Caenorhabditis elegans p53 family member CEP-1 is required for apoptosis induction in meiotic, late-stage pachytene germ cells in response to DNA damage and meiotic recombination failure. In an unbiased genetic screen for negative regulators of CEP-1, we found that increased activation of the C. elegans ERK orthologue MPK-1, resulting from either loss of the lip-1 phosphatase or activation of let-60 Ras, results in enhanced cep-1-dependent DNA damage induced apoptosis. We further show that MPK-1 is required for DNA damage-induced germ cell apoptosis. We provide evidence that MPK-1 signaling regulates the apoptotic competency of germ cells by restricting CEP-1 protein expression to cells in late pachytene. Restricting CEP-1 expression to cells in late pachytene is thought to ensure that apoptosis doesn't occur in earlier-stage cells where meiotic recombination occurs. MPK-1 signaling regulates CEP-1 expression in part by regulating the levels of GLD-1, a translational repressor of CEP-1, but also via a GLD-1-independent mechanism. In addition, we show that MPK-1 is phosphorylated and activated upon ionising radiation (IR) in late pachytene germ cells and that MPK-1-dependent CEP-1 activation may be in part direct, as these two proteins interact in a yeast two-hybrid assay. In summary, we report our novel finding that MAP kinase signaling controls CEP-1-dependent apoptosis by several different pathways that converge on CEP-1. Since apoptosis is also restricted to pachytene stage cells in mammalian germlines, analogous mechanisms regulating p53 family members are likely to be conserved throughout evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

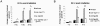
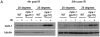
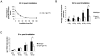

Similar articles
-
Reevaluation of the role of LIP-1 as an ERK/MPK-1 dual specificity phosphatase in the C. elegans germline.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jan 18;119(3):e2113649119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2113649119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35022236 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination of Recombination with Meiotic Progression in the Caenorhabditis elegans Germline by KIN-18, a TAO Kinase That Regulates the Timing of MPK-1 Signaling.Genetics. 2016 Jan;202(1):45-59. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.177295. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 26510792 Free PMC article.
-
The candidate MAP kinase phosphorylation substrate DPL-1 (DP) promotes expression of the MAP kinase phosphatase LIP-1 in C. elegans germ cells.Dev Biol. 2008 Apr 1;316(1):50-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.12.042. Epub 2008 Jan 8. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18304523 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for studying the DNA damage response in the Caenorhabdatis elegans germ line.Methods Cell Biol. 2012;107:321-52. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394620-1.00011-4. Methods Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22226529 Review.
-
RTK/Ras/MAPK signaling.WormBook. 2006 Feb 11:1-19. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.80.1. WormBook. 2006. PMID: 18050474 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oocyte aging is controlled by mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling.Aging Cell. 2021 Jun;20(6):e13386. doi: 10.1111/acel.13386. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Aging Cell. 2021. PMID: 34061407 Free PMC article.
-
DNA repair, recombination, and damage signaling.Genetics. 2022 Feb 4;220(2):iyab178. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab178. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35137093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3,3'-Diindolylmethane Supplementation Maintains Oocyte Quality by Reducing Oxidative Stress and CEP-1/p53-Mediated Regulation of Germ Cells in a Reproductively Aged Caenorhabditis elegans Model.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 11;11(5):950. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050950. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624814 Free PMC article.
-
The meiotic checkpoint network: step-by-step through meiotic prophase.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Oct 1;6(10):a016675. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016675. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25274702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MPK-1/ERK pathway regulates DNA damage response during development through DAF-16/FOXO.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 6;46(12):6129-6139. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky404. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29788264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suh EK, Yang A, Kettenbach A, Bamberger C, Michaelis AH, et al. p63 protects the female germ line during meiotic arrest. Nature. 2006;444:624–628. - PubMed
-
- Schumacher B, Hofmann K, Boulton S, Gartner A. The C. elegans homolog of the p53 tumor suppressor is required for DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Curr Biol. 2001;11:1722–1727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

