Mediator subunit 12 is required for neutrophil development in zebrafish
- PMID: 21901140
- PMCID: PMC3162013
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023845
Mediator subunit 12 is required for neutrophil development in zebrafish
Abstract
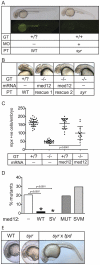
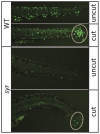
Hematopoiesis requires the spatiotemporal organization of regulatory factors to successfully orchestrate diverse lineage specificity from stem and progenitor cells. Med12 is a regulatory component of the large Mediator complex that enables contact between the general RNA polymerase II transcriptional machinery and enhancer bound regulatory factors. We have identified a new zebrafish med12 allele, syr, with a single missense mutation causing a valine to aspartic acid change at position 1046. Syr shows defects in hematopoiesis, which predominantly affect the myeloid lineage. Syr has identified a hematopoietic cell-specific requirement for Med12, suggesting a new role for this transcriptional regulator.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Conaway R, Sato S, Tomomorisato C, Yao T, Conaway J. The mammalian Mediator complex and its role in transcriptional regulation. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 2005;30:250–255. - PubMed
-
- Malik S, Roeder R. Dynamic regulation of pol II transcription by the mammalian Mediator complex. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 2005;30:256–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

