Agents increasing cyclic GMP amplify 5-HT4-elicited positive inotropic response in failing rat cardiac ventricle
- PMID: 21901315
- PMCID: PMC3220808
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-011-0670-6
Agents increasing cyclic GMP amplify 5-HT4-elicited positive inotropic response in failing rat cardiac ventricle
Abstract
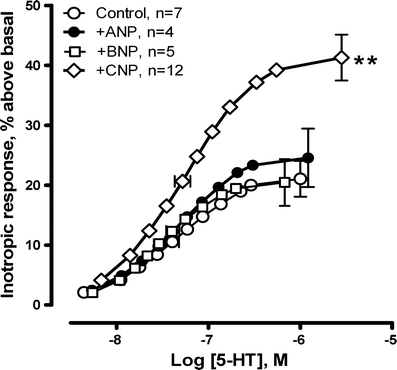
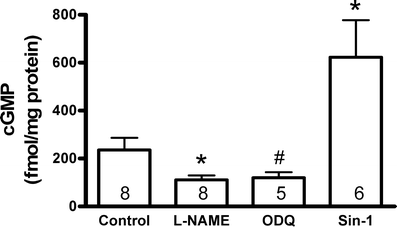
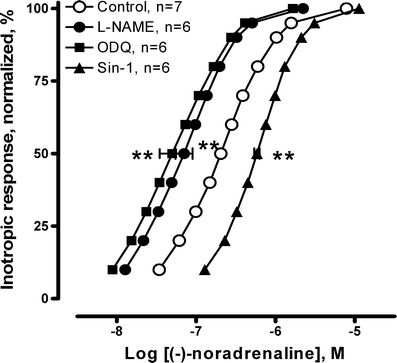
Activation of 5-HT(4) receptors in failing ventricles elicits a cAMP-dependent positive inotropic response which is mainly limited by the cGMP-inhibitable phosphodiesterase (PDE) 3. However, PDE4 plays an additional role which is demasked by PDE3 inhibition. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of cGMP generated by particulate and soluble guanylyl cyclase (GC) on the 5-HT(4)-mediated inotropic response. Extensive myocardial infarctions were induced by coronary artery ligation in Wistar rats, exhibiting heart failure 6 weeks after surgery. Contractility was measured in left ventricular preparations. Cyclic GMP was measured by EIA. In ventricular preparations, ANP or BNP displayed no impact on 5-HT(4)-mediated inotropic response. However, CNP increased the 5-HT(4)-mediated inotropic response as well as the β(1)-adrenoceptor (β(1)-AR)-mediated response to a similar extent as PDE3 inhibition by cilostamide. Pretreatment with cilostamide eliminated the effect of CNP. Inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) synthase and soluble GC by L-NAME and ODQ, respectively, attenuated the 5-HT(4)-mediated inotropic response, whereas the NO donor Sin-1 increased this response. The effects were absent during PDE3 inhibition, suggesting cGMP-dependent inhibition of PDE3. However, in contrast to the effects on the 5-HT(4) response, Sin-1 inhibited whereas L-NAME and ODQ enhanced the β(1)-AR-mediated inotropic response. cGMP generated both by particulate (NPR-B) and soluble GC increases the 5-HT(4)-mediated inotropic response in failing hearts, probably through inhibition of PDE3. β(1)-AR and 5-HT(4) receptor signalling are subject to opposite regulatory control by cGMP generated by soluble GC in failing hearts. Thus, cGMP from different sources is functionally compartmented, giving differential regulation of different G(s)-coupled receptors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phosphodiesterases and Compartmentation of cAMP and cGMP Signaling in Regulation of Cardiac Contractility in Normal and Failing Hearts.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 15;23(4):2145. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042145. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-HT4-elicited positive inotropic response is mediated by cAMP and regulated by PDE3 in failing rat and human cardiac ventricles.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Dec;155(7):1005-14. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.339. Epub 2008 Sep 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18846035 Free PMC article.
-
PDE3 inhibition by C-type natriuretic peptide-induced cGMP enhances cAMP-mediated signaling in both non-failing and failing hearts.Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Oct 5;812:174-183. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.07.014. Epub 2017 Jul 8. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28697992
-
Study of the regulation of the inotropic response to 5-HT4 receptor activation via phosphodiesterases and its cross-talk with C-type natriuretic peptide in porcine left atrium.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;385(6):565-77. doi: 10.1007/s00210-012-0746-y. Epub 2012 Mar 17. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22426996
-
Regulation and therapeutic targeting of peptide-activated receptor guanylyl cyclases.Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Apr;130(1):71-82. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.12.005. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21185863 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of phosphodiesterases and cGMP on cAMP generation and on phosphorylation of phospholamban and troponin I by 5-HT4 receptor activation in porcine left atrium.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;386(8):671-84. doi: 10.1007/s00210-013-0855-2. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23549671
-
Role of phosphodiesterase 1 in the pathophysiology of diseases and potential therapeutic opportunities.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Oct;226:107858. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107858. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33895190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphodiesterase in heart and vessels: from physiology to diseases.Physiol Rev. 2024 Apr 1;104(2):765-834. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00015.2023. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37971403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphodiesterases and Compartmentation of cAMP and cGMP Signaling in Regulation of Cardiac Contractility in Normal and Failing Hearts.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 15;23(4):2145. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042145. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac PDEs and crosstalk between cAMP and cGMP signalling pathways in the regulation of contractility.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;386(8):665-70. doi: 10.1007/s00210-013-0874-z. Epub 2013 May 7. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23649864
References
-
- Afzal F, Andressen KW, Mørk HK, Aronsen JM, Sjaastad I, Dahl CP, Skomedal T, Levy FO, Osnes JB, Qvigstad E. 5-HT4-elicited positive inotropic response is mediated by cAMP and regulated by PDE3 in failing rat and human cardiac ventricles. Br J Pharmacol. 2008;155:1005–1014. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.339. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Afzal F, Aronsen JM, Moltzau LR, Sjaastad I, Levy FO, Skomedal T, Osnes JB, Qvigstad E. Differential regulation of β2-adrenoceptor-mediated inotropic and lusitropic response by PDE3 and PDE4 in failing and non-failing rat cardiac ventricle. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;162:54–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00890.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bendall JK, Damy T, Ratajczak P, Loyer X, Monceau V, Marty I, Milliez P, Robidel E, Marotte F, Samuel JL, Heymes C. Role of myocardial neuronal nitric oxide synthase-derived nitric oxide in β-adrenergic hyporesponsiveness after myocardial infarction-induced heart failure in rat. Circulation. 2004;110:2368–2375. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000145160.04084.AC. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brattelid T, Qvigstad E, Lynham JA, Molenaar P, Aass H, Geiran O, Skomedal T, Osnes J-B, Levy FO, Kaumann AJ. Functional serotonin 5-HT4 receptors in porcine and human ventricular myocardium with increased 5-HT4 mRNA in heart failure. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol. 2004;370:157–166. doi: 10.1007/s00210-004-0963-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

