Emotional cues enhance the attentional effects on spatial and temporal resolution
- PMID: 21901512
- PMCID: PMC3219868
- DOI: 10.3758/s13423-011-0156-z
Emotional cues enhance the attentional effects on spatial and temporal resolution
Abstract
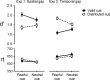
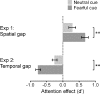
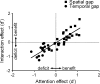
In the present study, we demonstrated that the emotional significance of a spatial cue enhances the effect of covert attention on spatial and temporal resolution (i.e., our ability to discriminate small spatial details and fast temporal flicker). Our results indicated that fearful face cues, as compared with neutral face cues, enhanced the attentional benefits in spatial resolution but also enhanced the attentional deficits in temporal resolution. Furthermore, we observed that the overall magnitudes of individuals' attentional effects correlated strongly with the magnitude of the emotion × attention interaction effect. Combined, these findings provide strong support for the idea that emotion enhances the strength of a cue's attentional response.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of auditory spatial attention by visual emotional cues: differential effects of attentional engagement and disengagement for pleasant and unpleasant cues.Cogn Process. 2016 May;17(2):205-11. doi: 10.1007/s10339-016-0749-6. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Cogn Process. 2016. PMID: 26842012
-
Asymmetries in the covert orienting of visual spatial attention to spatial and non-spatial cues in Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 1995 Dec;118 ( Pt 6):1421-35. doi: 10.1093/brain/118.6.1421. Brain. 1995. PMID: 8595474
-
Seeing fearful body language overcomes attentional deficits in patients with neglect.J Cogn Neurosci. 2007 Mar;19(3):445-54. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2007.19.3.445. J Cogn Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17335393
-
Dynamics of emotional effects on spatial attention in the human visual cortex.Prog Brain Res. 2006;156:67-91. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)56004-2. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17015075 Review.
-
Covert attention effects on spatial resolution.Prog Brain Res. 2009;176:65-86. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(09)17605-7. Prog Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19733750 Review.
Cited by
-
Fearful faces heighten the cortical representation of contextual threat.Neuroimage. 2014 Feb 1;86:317-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.10.008. Epub 2013 Oct 12. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24125792 Free PMC article.
-
How arousal modulates the visual contrast sensitivity function.Emotion. 2014 Oct;14(5):978-84. doi: 10.1037/a0037047. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Emotion. 2014. PMID: 24932842 Free PMC article.
-
No prior entry for threat-related faces: evidence from temporal order judgments.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 30;8(4):e62296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062296. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23646126 Free PMC article.
-
How Does Fearful Emotion Affect Visual Attention?Front Psychol. 2021 Jan 8;11:584412. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.584412. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33488451 Free PMC article.
-
Cumulative activation during positive and negative events and state anxiety predicts subsequent inertia of amygdala reactivity.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2015 Feb;10(2):180-90. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsu044. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 24603023 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

