Intravenous or enteral loop diuretics for preterm infants with (or developing) chronic lung disease
- PMID: 21901676
- PMCID: PMC7055198
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001453.pub2
Intravenous or enteral loop diuretics for preterm infants with (or developing) chronic lung disease
Abstract
Background: Lung disease in preterm infants is often complicated with lung edema.
Objectives: To assess the risks and benefits of administration of a diuretic acting on the loop of Henle (loop diuretic) in preterm infants with or developing chronic lung disease (CLD).
Search strategy: Standard search method of the Cochrane Neonatal Review Group was used. Initial search included the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL, The Cochrane Library, Issue 1, 2003), MEDLINE (1966 to April 2003), EMBASE (1974 to 1998). In addition, several abstract books of national and international American and European Societies were hand searched. The MEDLINE and the Cochrane Central searches were updated in March 2007 and December 2010. The EMBASE search was completed in April 2007 and December 2010. Additional searches in CINAHL, clinicaltrials.gov and controlled-trials.com was completed in December 2010.
Selection criteria: Trials in which preterm infants with or developing chronic lung disease and at least five days of age were all randomly allocated to receive a loop diuretic either enterally or intravenously were included in this analysis.
Data collection and analysis: The standard method for the Cochrane Collaboration described in the Cochrane Collaboration Handbook were used. Two investigators extracted, assessed and coded separately all data for each study. Parallel and cross-over trials were combined and, whenever possible, transformed baseline and final outcome data measured on a continuous scale into change scores using Follmann's formula.
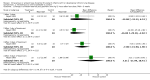
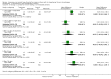
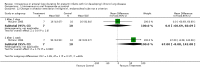
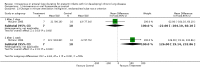
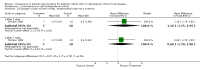
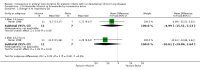
Main results: The only loop diuretic used in the six studies that met the selection criteria was furosemide. Most studies focused on pathophysiological parameters and did not assess effects on important clinical outcomes defined in this review, or the potential complications of diuretic therapy. In preterm infants < 3 weeks of age developing CLD, furosemide administration has either inconsistent effects or no detectable effect. In infants > 3 weeks of age with CLD, a single intravenous dose of 1 mg/kg of furosemide improves lung compliance and airway resistance for one hour. Chronic administration of furosemide improves both oxygenation and lung compliance.
Authors' conclusions: In view of the lack of data from randomized trials concerning effects on important clinical outcomes, routine or sustained use of systemic loop diuretics in infants with (or developing) CLD cannot be recommended based on current evidence. Randomized trials are needed to assess the effects of furosemide administration on survival, duration of ventilatory support and oxygen administration, length of hospital stay, potential complications and long-term outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures















Update of
-
Intravenous or enteral loop diuretics for preterm infants with (or developing) chronic lung disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(1):CD001453. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001453. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Sep 07;(9):CD001453. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001453.pub2. PMID: 11869600 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Kao 1983 {published data only}
-
- Kao LC, Warburton D, Sargent CW, Platzker AC, Keens TG. Furosemide acutely decreases airways resistance in chronic bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Journal of Pediatrics 1983;103:624‐9. - PubMed
McCann 1985 {published data only}
-
- McCann EM, Lewis K, Deming DD, Donovan MJ, Brady JP. Controlled trial of furosemide therapy in infants with chronic lung disease. Journal of Pediatrics 1985;106:957‐62. - PubMed
Najak 1983 {published data only}
-
- Najak ZD, Harris EM, Lazzara A, Pruitt AW. Pulmonary effects of furosemide in preterm infants with lung disease. Journal of Pediatrics 1983;102:758‐63. - PubMed
Reiter 1998 {published data only}
-
- Reiter PD, Makhlouf R, Stiles AD. Comparison of 6‐hour infusion versus bolus furosemide in premature infants. Pharmacotherapy ‐ The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy 1998;18:63‐8. - PubMed
Rush 1990 {published data only}
-
- Rush MG, Engelhardt B, Parker RA, Hazinski TA. Double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of alternate‐day furosemide therapy in infants with chronic bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Journal of Pediatrics 1990;117:112‐8. - PubMed
Singhal 1983 {published data only}
-
- Singhal N, McMillan DD, Rademaker AW. Furosemide improves lung compliance in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia [abstract]. Pediatric Research 1983;17:336A.
References to studies excluded from this review
Atkinson 1988 {published data only}
-
- Atkinson SA, Shah JK, McGee C, Steele BT. Mineral excretion in premature infants receiving various diuretic therapies. Journal of Pediatrics 1988;113:540‐5. - PubMed
Braden 1997 {published data only}
-
- Braden G, Campfield T, Flynn‐Valone P, Bednarek F, Pappagallo M. Nephrocalcinosis in very low birthweight infants: a prospective multicenter study of risk factors and complications [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1997;8:122A.
Campfield 1997 {published data only}
-
- Campfield T, Braden G, Flynn‐Valone P, Powell S. Effect of diuretics on urinary oxalate, calcium, and sodium excretion in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 1997;99:814‐8. - PubMed
Engelhardt 1986 {published data only}
-
- Engelhardt B, Elliott S, Hazinski TA. Short‐ and long‐term effects of furosemide on lung function in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Journal of Pediatrics 1986;109:1034‐9. - PubMed
Giacoia 1991 {published data only}
-
- Giacoia GP, Pineda R. Diuretics, hypochloremia, and outcome in bronchopulmonary dysplasia patients. Developmental Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1991;4:212‐20. - PubMed
Kenney 1988 {published data only}
-
- Kenney IJ, Aiken CG, Lenney W. Frusemide‐induced nephrocalcinosis in very low weight infants. Pediatric Radiology 1988;18:323‐5. - PubMed
Logvinoff 1985 {published data only}
-
- Logvinoff MM, Lemen RJ, Taussig LM, Lamont BA. Bronchodilators and diuretics in children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatric Pulmonology 1985;1:198‐203. - PubMed
Mirochnick 1988 {published data only}
-
- Mirochnick MH, Miceli JJ, Kramer PA, Chapron DJ, Raye JR. Furosemide pharmacokinetics in very low birth weight infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1988;112:653‐7. - PubMed
Mirochnick 1990 {published data only}
-
- Mirochnick MH, Miceli JJ, Kramer PA, Chadron DJ, Raye JR. Renal response to furosemide in very low birth weight infants during chronic administration. Developmental Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1990;15:1‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
O'Donovan 1989 {published data only}
-
- O'Donovan BH, Bell EF. Effects of furosemide on body water compartments in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatric Research 1989;26:121‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Patel 1985 {published data only}
-
- Patel H, Yeh TF, Jain R, Pildes R. Pulmonary and renal responses to furosemide in infants with stage III‐IV bronchopulmonary dysplasia. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1985;139:917‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Perlman 1986 {published data only}
-
- Perlman JM, Moore V, Siegel MJ, Dawson J. Is chloride depletion an important contributing cause of death in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia?. Pediatrics 1986;77:121‐216. - PubMed
Rowe 1989 {published data only}
-
- Rowe JC, Carey DE, Goetz CA, Adams ND, Horak E. Effect of high calcium and phosphorus intake on mineral retention in very low birth weight infants chronically treated with furosemide. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1989;9:206‐11. - PubMed
Segar 1992 {published data only}
-
- Segar JL, Robillard JE, Johnson KJ, Bell EF, Chemtob S. Addition of metolazone to overcome tolerance to furosemide in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Journal of Pediatrics 1992;120:966‐73. - PubMed
Segar 1997 {published data only}
-
- Segar JL, Chemtob S, Bell EF. Changes in body water compartments with diuretic therapy in infants with chronic lung disease. Early Human Development 1997;48:99‐107. - PubMed
Shankaran 1994 {published data only}
-
- Shankaran S, Liang KC, Ilagan N, Fleischmann L. Mineral excretion following furosemide compared with bumetanide therapy in premature infants. Pediatric Nephrology 1995;9:159‐62. - PubMed
Sniderman 1978 {published data only}
-
- Sniderman S, Chung M, Roth R, Ballard R. Treatment of neonatal chronic lung disease with furosemide [abstract]. Clinical Research 1978; Vol. 26:201A.
Stefano 1990 {published data only}
-
- Stefano JL, Bhutani VK. Role of furosemide therapy after booster‐packed erythrocyte transfusions in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Journal of Pediatrics 1990;117:965‐8. - PubMed
-
- Stefano JL, Bhutani VK. The effect of furosemide on pulmonary function following booster transfusions in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. American Journal of Perinatology 1990; Vol. 7:393.
Verma 1994 {published data only}
-
- Verma RP, Fornell JE, Vidyasagar D. Body fluid electrolytes in bronchopulmonary dysplasia and the effects of diuretic therapy. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 1994;61:213‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vileisis 1990 {published data only}
-
- Vileisis RA. Furosemide effect on mineral status of parenterally nourished premature neonates with chronic lung disease. Pediatrics 1990;85:316‐22. - PubMed
Yeh 1984 {published data only}
-
- Yeh TF, Jain R, Patel H, Pildes RS. Renal response to furosemide in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia [abstract]. Pediatric Research 1984; Vol. 18:340A.
Additional references
Abbasi 1990
-
- Abbasi S, Bhutani VK. Pulmonary mechanics and energetics of normal, non‐ventilated low birthweight infants. Pediatric Pulmonology 1990;8:89‐95. - PubMed
Ali 1979
Armitage 1994
-
- Armitage P, Berry G. Sampling. In: Armitage P, Berry G editor(s). Statistical Methods in Medical Research. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific, 1994:78‐92.
Aufricht 1997
-
- Aufricht C, Votava F, Marx M, Frenzel K, Simbruner G. Intratracheal furosemide in infants after cardiac surgery: its effects on lung mechanics and urinary output, and its levels in plasma and tracheal aspirate. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine 1997;23:992‐7. - PubMed
Baird 1995
-
- Baird DC. Statistics of observation. In: Baird DC editor(s). Experimentation. An introduction to measurement theory and experiment design. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1995:29‐56.
Bland 1978
Brion 1994
-
- Brion LP, Satlin LM, Edelmann CM Jr. Renal disease. In: Avery GB, Fletcher MA, MacDonald MG editor(s). Neonatology: Pathophysiology and Management of the Newborn. 4th Edition. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott, 1994:792‐886.
Brion 1998
Brion 1999b
Brion 1999c
Brion 1999d
Brown 1978
-
- Brown ER, Stark A, Sosenko I, Lawson EE, Avery ME. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: Possible relationship to pulmonary edema. Journal of Pediatrics 1978;92:982‐4. - PubMed
Campfield 1997
-
- Campfield T, Braden G, Flynn‐Valone P, Powell S. Effect of diuretics on urinary oxalate, calcium, and sodium excretion in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 1997;99:814‐8. - PubMed
Chemtob 1989
-
- Chemtob S, Kaplan BS, Sherbotie JR, Aranda JV. Pharmacology of diuretics in the newborn. The Pediatric Clinics of North America 1989;36:1231‐50. - PubMed
Clark 2006
-
- Clark RH, Bloom BT, Spitzer AR, Gerstmann DR. Reported medication use in the neonatal intensive care unit: data from a large national data set. Pediatrics 2006;117:1979‐87. - PubMed
Demling 1978
-
- Demling RH, Will JA. The effect of furosemide on the pulmonary transvascular fluid filtration rate. Critical Care Medicine 1978;6:317‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dikshit 1973
-
- Dikshit K, Vyden JK, Forrester JS, Chatterjee K, Prakash R, Swan HJ. Renal and extrarenal hemodynamic effects of furosemide in congestive heart failure after acute myocardial infarction. New England Journal of Medicine 1973;288:1087‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Downing 1992
-
- Downing GJ, Egelhoff JC, Daily DK, Thomas MK, Alon U. Kidney function in very low birth weight infants with furosemide‐related renal calcifications at ages 1 to 2 years. Journal of Pediatrics 1992;120:599‐604. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Edwards 1979
-
- Edwards DK, Colby TV, Northway WH. Radiographic‐pathologic correlation in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Journal of Pediatrics 1979;85:834‐6. - PubMed
Ezzedeen 1988
-
- Ezzedeen F, Adelman RD, Ahlfors CE. Renal calcification in preterm infants: pathophysiology and long‐term sequelae [comment in: J Pediatr 1989;114:1068]. Journal of Pediatrics 1988;113:532‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Follmann 1992
-
- Follmann D, Elliott P, Suh I, Cutler J. Variance imputation for overviews of clinical trials with continuous response. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1992;45:769‐73. - PubMed
Gerhardt 1989
-
- Gerhardt T, Reifenberg L, Duara S, Bancalari E. Comparison of dynamic and static measurements of respiratory mechanics in infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1989;114:120‐5. - PubMed
Giacoia 1991
-
- Giacoia GP, Pineda R. Diuretics, hypochloremia, and outcome in bronchopulmonary dysplasia patients. Developmental Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1991;4:212‐20. - PubMed
Gimpel 2010
-
- Gimpel C, Krause A, Franck P, Krueger M, Schnakenburg C. Exposure to furosemide as the strongest risk factor for nephrocalcinosis in preterm infants. Pediatrics International 2010;52:51‐6. - PubMed
Gortner 1991
-
- Gortner L, Bernsau U, Hellwege HH, Hieronimi G, Jorch G, Reiter HL. Does prophylactic use of surfactant change drug utilization in very premature infants during the neonatal period?. Developmental Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1991;16:1‐16. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Goyal 1995
-
- Goyal M, Suresh BR, Reinersman G, Gewolb IH, Brion LP. Evolution and variability of pulmonary mechanics during postnatal transition in full‐term infants. Journal of Perinatology 1995;15:441‐8. - PubMed
Green 1983
-
- Green TP, Thompson TR, Johnson DE, Lock JE. Furosemide promotes patent ductus arteriosus in premature infants with the respiratory‐distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 1983;308:743‐8. - PubMed
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins 2008. Cochrane Handbook.
Horgan 1996
-
- Horgan MJ. Thiazide‐induced hyponatremia in <1500 gm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia [abstract]. Pediatric Research 1996; Vol. 38:216A.
Kugelman 1996
-
- Kugelman A, McEvoy C, Bowling S, Durand M. Comparison of dynamic and passive measurements of respiratory dynamics during dexamethasone (Dex) treatment in very low birthweight (VLBW) infants [abstract]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1996; Vol. 153:A556.
LeSouef 1983
-
- LeSouëf PN, Lopes JM, England SJ, Bryan MH, Bryan AC. Influence of chest wall distortion on esophageal pressure. Journal of Applied Physiology 1983;55:353‐8. - PubMed
LeSouef 1984
-
- LeSouëf PN, England SJ, Bryan AC. Passive respiratory mechanics in newborns and children. The American Review of Respiratory Disease 1985;132:694‐709. - PubMed
Lopez 1990
-
- Lopez AM, Modi MW, Adams JA, Horner GP, Grazia FTR, Goldberg RN. Pharmacokinetics of bumetanide in the newborn infant [abstract]. Pediatric Research 1990; Vol. 27:62A.
Mirochnick 1988
-
- Mirochnick MH, Miceli JJ, Kramer PA, Chapron DJ, Raye JR. Furosemide pharmacokinetics in very low birth weight infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1988;112:653‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Northway 1967
-
- Northway WH, Rosan RC, Porter DY. Pulmonary disease following respiratory therapy of hyaline membrane disease: bronchopulmonary dysplasia. New England Journal of Medicine 1967;276:357‐68. - PubMed
O'Donovan 1989
-
- O'Donovan BH, Bell EF. Effects of furosemide on body water compartments in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatric Research 1989;26:121‐4. - PubMed
Perlman 1986
-
- Perlman JM, Moore V, Siegel MJ, Dawson J. Is chloride depletion an important contributing cause of death in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia?. Pediatrics 1986;77:212‐6. - PubMed
Peterson 1980
-
- Peterson RG, Simmons MA, Rumack BH, Levine RL, Brooks JG. Pharmacology of furosemide in the premature infant. Journal of Pediatrics 1980;97:139‐43. - PubMed
Randall 1992
-
- Randall LH, Shaddy RE, Sturtevant JE, Reid BS, Molteni RA. Cholelithiasis in infants receiving furosemide: a prospective study of the incidence and one‐year follow‐up. Journal of Perinatology 1992;12:107‐111. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Reid 1979
-
- Reid L. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia ‐ Pathology. Journal of Pediatrics 1979;85:836‐41. - PubMed
Robbins 1993
-
- Robbins G, Tayaba R, Ochshorn IL, Green RS, Holzman IR. Effects of nebulized furosemide vs normal saline on pulmonary mechanics in bronchopulmonary dysplasia [abstract]. Pediatric Research 1993; Vol. 33:233A.
Shankaran 1990
-
- Shankaran S, Ilagan N, Liang KC, Bhavsar V, Kauffman R. Bumetanide pharmacokinetics in preterm neonates [abstract]. Pediatric Research 1990; Vol. 27:64A.
Sola 1981
-
- Sola A, Gregory GA. Colloid osmotic pressure of normal newborns and premature infants. Critical Care Medicine 1981;9:568‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sonntag 1996
-
- Sonntag J. Effect of dexamethasone and spironolactone therapy on diuresis and creatinine clearance in premature infants with a birth weight below 1,500g. Klinische Padiatrie 1996;208:319‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Thomson 1983
Vert 1982
-
- Vert P, Broquaire M, Legagneur M, Morselli PL. Pharmacokinetics of furosemide in neonates. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1982;22:39‐45. - PubMed
Wilson 1981
-
- Wilson JR, Reichek N, Dunkman WB, Goldberg S. Effect of diuresis on the performance of the failing left ventricle in man. The American Journal of Medicine 1981;70:234‐9. - PubMed
Zimmerman 1995
-
- Zimmerman JJ. Bronchoalveolar inflammatory pathophysiology of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Clinical Perinatology 1995;22:429‐56. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Brion 1999a
-
- Brion LP, Primhak RA. Use of intravenous or oral furosemide (F) in preterm infants with or developing chronic lung disease (CLD): Systematic review and meta‐analysis [abstract]. Pediatric Research 1999; Vol. 45:296A.
Brion 2000
Brion 2001
Brion 2002
Brion 2003
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

