Antihistamines and/or decongestants for otitis media with effusion (OME) in children
- PMID: 21901683
- PMCID: PMC7170417
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003423.pub3
Antihistamines and/or decongestants for otitis media with effusion (OME) in children
Abstract
Background: This is an update of a Cochrane Review first published in The Cochrane Library in Issue 4, 2006.Otitis media with effusion (OME) is common and may cause hearing loss with associated developmental delay. Treatment remains controversial. The effectiveness of antihistamines, decongestants and antihistamine/decongestant combinations in promoting the resolution of effusions has been assessed by randomized controlled trials.
Objectives: The objective of this review was to determine whether antihistamine, decongestant or combination therapy is effective in treating children who present with OME.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders Group Trials Register; the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL); PubMed; EMBASE; CINAHL; Web of Science; BIOSIS Previews; Cambridge Scientific Abstracts; ISRCTN and additional sources for published and unpublished trials. The date of the most recent search was 1 February 2011, following a previous search in 2006.
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) using antihistamines, decongestants or antihistamine/decongestant combinations as treatment for OME in children. We excluded trials that randomized on the basis of acute otitis media (AOM) even though OME was also studied in follow up.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently extracted data from the published reports using standardized data extraction forms and methods. The two authors assessed the methodological quality of the included studies independently. We expressed dichotomous results as a risk ratio with 95% confidence intervals using a fixed-effect model when homogeneous and a random-effects model when heterogeneous. Nearly all outcomes analyzed were homogeneous. We discussed continuous results qualitatively. We conducted statistical analysis using RevMan 5.1 software.
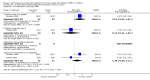
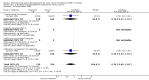
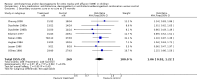
Main results: Sixteen studies (1880 participants) were included in the review. No statistical or clinical benefit was found for any of the interventions or outcomes studied. However, treated study subjects experienced 11% more side effects than untreated subjects (number needed to treat to harm = 9).
Authors' conclusions: The pooled data demonstrate no benefit and some harm from the use of antihistamines or decongestants alone or in combination in the management of OME, therefore we recommend against their use.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures

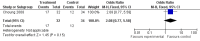


























Update of
-
Antihistamines and/or decongestants for otitis media with effusion (OME) in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Oct 18;(4):CD003423. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003423.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Sep 07;(9):CD003423. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003423.pub3. PMID: 17054169 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Cantekin 1983 {published data only}
-
- Cantekin EI, Mandel EM, Bluestone CD, Rockette HE, Paradise JL, Stool SE, et al. Lack of efficacy of a decongestant‐antihistamine combination for otitis media with effusion ("secretory" otitis media) in children. Results of a double‐blind, randomized trial. New England Journal of Medicine 1983;308(6):297‐301. - PubMed
Cantekin 1991 {published data only}
-
- Cantekin EI, McGuire TW, Griffith TL. Antimicrobial therapy for otitis media with effusion ('secretory' otitis media) [see comment]. JAMA 1991;266(23):3309‐17. - PubMed
-
- Mandel EM, Rockette HE, Bluestone CD, Paradise JL, Nozza RJ. Efficacy of amoxicillin with and without decongestant‐antihistamine for otitis media with effusion in children. Results of a double‐blind, randomized trial. New England Journal of Medicine 1987;316(8):432‐7. - PubMed
Choung 2008 {published data only}
Dusdieker 1985a {published data only}
-
- Dusdieker LB, Smith G, Booth BM, Woodhead JC, Milavetz G. The long‐term outcome of nonsuppurative otitis media with effusion. Clinical Pediatrics 1985;24(4):181‐6. - PubMed
Dusdieker 1985b {published data only}
-
- Dusdieker LB, Smith G, Booth BM, Woodhead JC, Milavetz G. The long‐term outcome of nonsuppurative otitis media with effusion. Clinical Pediatrics 1985;24(4):181‐6. - PubMed
Edstrom 1977 {published data only}
-
- Edstrom S, Lundin K, Jeppsson PH. Secretory otitis media. Aspects on treatment and control. ORL: Journal of Oto‐Rhino‐Laryngology and its Related Specialties 1977;39(2):68‐73. - PubMed
Fabian 1986 {published data only}
-
- Fabian P, Lonnerholm G, Jerrmark‐Tera IB, Kleberg A, Melander H. Effects and adverse effects of decongestants in otosalpingitis. Lakartidningen 1986;83(42):3508‐13. - PubMed
Fraser 1977 {published data only}
-
- Fraser JG, Mehta M, Fraser PA. The medical treatment of secretory otitis media. A clinical trial of three commonly used regimes. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1977;91(9):757‐65. - PubMed
Haugeto 1981a {published data only}
-
- Haugeto OK, Schroder KE, Mair IW. Secretory otitis media, oral decongestant and antihistamine. Journal of Otolaryngology 1981;10(5):359‐62. - PubMed
Haugeto 1981b {published data only}
-
- Haugeto OK, Schroder KE, Mair IW. Secretory otitis media, oral decongestant and antihistamine. Journal of Otolaryngology 1981;10(5):359‐62. - PubMed
Hayden 1984 {published data only}
-
- Hayden GF, Randall JE, Randall JC, Hendley JO. Topical phenylephrine for the treatment of middle ear effusion. Archives of Otolaryngology 1984;110(8):512‐4. - PubMed
Hughes 1984 {published data only}
-
- Hughes KB. Management of middle‐ear effusions in children. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1984;98(7):677‐84. - PubMed
Khan 1981 {published data only}
-
- Khan JA, Marcus P, Cummings SW. S‐carboxymethylcysteine in otitis media with effusion (a double‐blind study). Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1981;95(10):995‐1001. - PubMed
Lesser 1986 {published data only}
-
- Lesser TH, Clayton MI, Skinner D. Efficacy of medical treatment as an adjunct to surgery in the treatment of secretory otitis media. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1986;100(12):1347‐50. - PubMed
O'Shea 1980 {published data only}
-
- O'Shea JS, Langenbrunner DJ, McCloskey DE, Pezzullo JC, Regan JB. Diagnostic and therapeutic studies in childhood serous otitis media. Results of treatment with an antihistamine‐adrenergic combination. Annals of Otology, Rhinology, and Laryngology. Supplement 1980;89(3 Pt 2):285‐9. - PubMed
O'Shea 1982 {published data only}
-
- O'Shea JS, Langenbrunner DJ, McCloskey DE, Pezzullo JC, Regan JB. Childhood serous otitis media: fifteen months' observations of children untreated compared with those receiving an antihistamine‐adrenergic combination. Clinical Pediatrics 1982;21(3):150‐3. - PubMed
Olson 1978 {published data only}
-
- Olson AL, Klein SW, Charney E, MacWhinney JB Jr, McInerny TK, Miller RL, et al. Prevention and therapy of serous otitis media by oral decongestant: a double‐blind study in pediatric practice. Pediatrics 1978;61(5):679‐84. - PubMed
Saunte 1978 {published data only}
-
- Saunte C. Clinical trial with Lunerin mixture and Lunerin mite in children with secretory otitis media. Journal of International Medical Research 1978;6(1):50‐5. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Altman 1998 {published data only}
-
- Altman JS, Haupert MS, Hamaker RA, Belenky WM. Phenylephrine and the prevention of postoperative tympanostomy tube obstruction. Archives of Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 1998;124(11):1233‐6. - PubMed
Bhambhani 1983 {published data only}
-
- Bhambhani K, Foulds DM, Swamy KN, Eldis FE, Fischel JE. Acute otitis media in children: are decongestants or antihistamines necessary?. Annals of Emergency Medicine 1983;12(1):13‐6. - PubMed
Brown 1985 {published data only}
-
- Brown DT, Potsic WP, Marsh RR, Litt M. Drugs affecting clearance of middle ear secretions: a perspective for the management of otitis media with effusion. Annals of Otology, Rhinology, and Laryngology. Supplement 1985;117:3‐15. - PubMed
Brownoff 1998 {published data only}
Cantekin 1980 {published data only}
-
- Cantekin EI, Bluestone CD, Rockette HE, Beery QC. Effect of decongestant with or without antihistamine on Eustachian tube function. Annals of Otology, Rhinology, and Laryngology. Supplement 1980;89(3 Pt 2):290‐5. - PubMed
Chonmaitree 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chonmaitree T, Saeed K, Uchida T, Heikkinen T, Baldwin CD, Freeman DH Jr, et al. A randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of the effect of antihistamine or corticosteroid treatment in acute otitis media. Journal of Pediatrics 2003;143(3):377‐85. - PubMed
Collins 1983 {published data only}
-
- Collins MP, Church MK. The effect of an anti‐allergic, nasal decongestant combination ('Dimotapp') and sodium cromoglycate nose drops on the histamine content of adenoids, middle ear fluid and nasopharyngeal secretions of children with secretory otitis media. Current Medical Research and Opinion 1983;8(4):392‐4. - PubMed
Gates 1986 {published data only}
-
- Gates GA, Wachtendorf C, Holt GR, Hearne EM. Medical treatment of chronic otitis media with effusion (secretory otitis media). Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 1986;94(3):350‐4. - PubMed
Grundfast 1981 {published data only}
-
- Grundfast KM. A review of the efficacy of systemically administered decongestants in the prevention and treatment of otitis media. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 1981;89(3 Pt 1):432‐9. - PubMed
Kjellman 1978 {published data only}
-
- Kjellman NI, Harder H, Lindwall L, Synnerstad B. Longterm treatment with brompheniramine and phenylpropanolamine in recurrent otitis media ‐ a double‐blind study. Journal of Otolaryngology 1978;7(3):257‐61. - PubMed
Klein 1980 {published data only}
-
- Klein SW, Olson AL, Perrin J, Cunningham D, Hengerer A, Hoekelman RA, et al. Prevention and treatment of serous otitis media with an oral antihistamine. A double‐blind study in pediatric practice. Clinical Pediatrics 1980;19(5):342‐7. - PubMed
Kraemer 1984 {published data only}
-
- Kraemer MJ, Marshall SG, Richardson MA. Etiologic factors in the development of chronic middle ear effusions. Clinical Reviews in Allergy 1984;2(4):319‐28. - PubMed
Lildholdt 1982 {published data only}
-
- Lildholdt T, Cantekin EI, Bluestone CD, Rockette HE. Effect of a topical nasal decongestant on Eustachian tube function in children with tympanostomy tubes. Acta Oto‐Laryngologica 1982;94(1‐2):93‐7. - PubMed
Malm 1985 {published data only}
-
- Malm L. Oral decongestants in acute rhinitis, acute sinusitis, acute otitis media and secretory otitis media: prognostic implications. Workshop: Treatment of Ear, Nose and Throat Infections. 1985.
Marshall 1984 {published data only}
-
- Marshall SG, Bierman CW, Shapiro GG. Otitis media with effusion in childhood. Annals of Allergy 1984;53(5):370‐8, 394. - PubMed
McCormick 2003 {published data only}
-
- McCormick DP, Saeed K, Uchida T, Baldwin CD, Deskin R, Lett‐Brown MA, et al. Middle ear fluid histamine and leukotriene B4 in acute otitis media: effect of antihistamine or corticosteroid treatment. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 2003;67(3):221‐30. - PubMed
Moller 1980 {published data only}
-
- Moller P. Negative middle ear pressure and hearing thresholds in secretory otitis media. A double‐blind crossover study with Lunerin. Scandinavian Audiology 1980;9(3):171‐6. - PubMed
Moran 1982 {published data only}
-
- Moran DM, Mutchie KD, Higbee MD, Paul LD. The use of an antihistamine‐decongestant in conjunction with an anti‐infective drug in the treatment of acute otitis media. Journal of Pediatrics 1982;101(1):132‐6. - PubMed
Ogino 1992 {published data only}
-
- Ogino S, Harada T, Matsunaga T, Tominaga Y. Use of Tranilast [N‐(3,4‐dimethoxycinnamoyl) anthranilic acid] in secretory otitis media. Annals of Allergy 1992;68(5):407‐12. - PubMed
Otten 1990 {published data only}
-
- Otten FW, Grote JJ. Otitis media with effusion and chronic upper respiratory tract infection in children: a randomized, placebo‐controlled clinical study. Laryngoscope 1990;100(6):627‐33. - PubMed
Sorri 1982 {published data only}
-
- Sorri M, Sipila P. Can secretory otitis media be prevented by oral decongestants?. Acta Otolaryngologica Supplement 1982;386:115‐6.
Suzuki 1999 {published data only}
-
- Suzuki M, Kawauchi H, Mogi G. Clinical efficacy of an antiallergic drug on otitis media with effusion in association with allergic rhinitis. Auris Nasus Larynx 1999;26(2):123‐9. - PubMed
Theoharides 1994 {published data only}
-
- Theoharides TC, Manolidis SS, Vliagoftis H, Manolidis LS. Treatment of secretory otitis media with local instillation of hydroxyzine. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology 1994;103(1):95‐101. - PubMed
van Heerbeek 2002 {published data only}
-
- Heerbeek N, Ingels KJ, Zielhuis GA. No effect of a nasal decongestant on Eustachian tube function in children with ventilation tubes. Laryngoscope 2002;112(6):1115‐8. - PubMed
Additional references
AAFP 2004
-
- American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Otolaryngology ‐ Head, Neck Surgery. American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Otitis Media with Effusion. Otitis media with effusion. Pediatrics 2004;113(5):1412‐29. - PubMed
Bandolier 2000
-
- Bandolier Bias Guide. http://www.medicine.ox.ac.uk/bandolier/Extraforbando/Bias.pdf 2000 (accessed 11 October 2010).
Barker 2005
-
- Barker FG, Carter BS. Synthesizing medical evidence: systematic reviews and meta‐analyses. Neurosurgical Focus 2005;19(E5):1‐21. - PubMed
Becker 2011
Berlin 1997
-
- Berlin J. Does blinding of readers affect the results of meta‐analyses?. Lancet 1997;350:185‐6. - PubMed
Bluestone 1995
-
- Bluestone CD, Klein JO. Otitis Media in Infants and Children. Second Edition. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 1995.
Browning 2010
Fiellau 1977
-
- Fiellau‐Nikolajsen M, Lous J, Pedersen SV, Schousboe HH. Tympanometry in three‐year‐old children. 1. A regional prevalence study on the distribution of tympanometric results in a non‐selected population of three‐year‐old children. Scandinavian Audiology 1977;6:199‐204. - PubMed
Fiellau 1979
-
- Fiellau‐Nikolajsen M, Lous J. Prospective tympanometry in three‐year‐old children: a study of spontaneous course of tympanometry types in a non‐selected population. Archives of Otolaryngology 1979;105:461‐6. - PubMed
Fiellau 1983
-
- Fiellau‐Nikolajsen M. Tympanometry and secretory otitis media. Observations on diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment, and prevention in prospective cohort studies of three‐year‐old children [thesis]. Acta Otolaryngologica Stockholm Supplement 1983;394:1‐73. - PubMed
Golz 1998
-
- Golz A Netzer A, Angel‐Yeger B, Westerman ST, Gilbert LM, Joachims HZ. Effects of middle ear effusions on the vestibular system in children. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 1998;119:695‐9. - PubMed
Grace 1990
-
- Grace AR, Pfleiderer AG. Dysequilibrium and otitis media with effusion: what is the association?. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1990;104:682‐4. - PubMed
Handbook 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad A, Moore R, Carroll D. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17:1‐12. - PubMed
Lexi‐Drugs 2006
-
- Lexi‐Drugs. http://www.cma.ca/index.cfm?la_id=1&ci_id=370&gmAction=/lexidrug... (accessed 27 June 2006).
Lous 1981
-
- Lous J, Fiellau‐Nikolajsen M. Epidemiology of middle ear effusion and tubal dysfunction: a one‐year prospective study comprising monthly tympanometry in 387 non‐selected 7‐year‐old children. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 1981;3:303‐17. - PubMed
Lous 1995
-
- Lous J. Secretory otitis media in schoolchildren. Is screening for secretory otitis media advisable?. Danish Medical Bulletin 1995;42:71‐99. - PubMed
Mohar 1995
-
- Mohar D, Jadad AR, Nichol G. Assessing the quality of randomized controlled trials: an annotated bibliography of scales and checklists. Controlled Clinical Trials 1995;16:62‐73. - PubMed
Perera 2006a
-
- Perera R, Glasziou P. Design effect adjustment for paired data. (submitted to Statistics in Medicine) 2006.
Perera 2006b
Rosenfeld 1999
-
- Rosenfeld R, Bluestone C. Evidence Based Otitis Media. Hamilton, Ontario: BC Decker, 1999.
Shekelle 2003
-
- Shekelle P, Takata G, Chan LS, Mangione‐Smith R, Corley PM, Morphew T, et al. Diagnosis, natural history, and late effects of otitis media with effusion. Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 55 (Prepared by Southern California Evidence‐based Practice Center under Contract No 290‐97‐0001, Task Order No. 4). AHRQ Publication No. 03‐E023. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality May 2003.
Simpson 2011
Takata 2003
-
- Takata GS, Chan LS, Morphew T, Mangione‐Smith R, Morton SC, Shekelle P. Evidence assessment of the accuracy of methods of diagnosing middle ear effusion in children with otitis media with effusion. Pediatrics 2003;112(6 Pt 1):1379‐87. - PubMed
Teele 1989
-
- Teele DW, Klein JO, Rosner B. Epidemiology of otitis media during the first seven years of life in children in greater Boston: a prospective, cohort study. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1989;160:83‐94. - PubMed
van den Aardweg 2010
Witmer 1998
-
- Witmer A, Wells AM, Seymour RJ. A comparison of the effectiveness of pharmacologic treatment of otitis media with effusion in children: integrative and meta‐analysis. Online Journal of Knowledge Synthesis for Nursing 1998; Vol. 5, issue 4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

